10-K: Annual report pursuant to Section 13 and 15(d)
Published on March 8, 2017
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
|
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016
Commission File Number 0-21886
BARRETT BUSINESS SERVICES, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Maryland |
|
52-0812977 |
|
(State or other jurisdiction of |
|
(IRS Employer |
|
incorporation or organization) |
|
Identification No.) |
|
|
|
|
|
8100 NE Parkway Drive, Suite 200 |
|
|
|
Vancouver, Washington |
|
98662 |
|
(Address of principal executive offices) |
|
(Zip Code) |
(360) 828-0700
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Title of each class |
|
Name of each exchange on which registered |
|
Common Stock, Par Value $0.01 Per Share |
|
The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company (as indicated by Exchange Act Rule 12b-2).
|
Large accelerated filer ☐ |
Accelerated filer ☒ |
Non-accelerated filer ☐ |
Smaller reporting company ☐ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
State the aggregate market value of the common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant: $289,288,504 at June 30, 2016
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant's classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date:
|
Class |
Outstanding at March 1, 2017 |
|
Common Stock, Par Value $.01 Per Share |
7,251,024 Shares |
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the definitive Proxy Statement for the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are hereby incorporated by reference in Part III of Form 10-K.
BARRETT BUSINESS SERVICES, INC.
2016 ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
|
PART I |
|
Page |
|
Item 1. |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1A. |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1B. |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 2. |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 3. |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 4. |
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5. |
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 6. |
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 7. |
|
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 7A. |
|
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 8. |
|
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 9. |
|
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 9A. |
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 9B. |
|
|
51 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 10. |
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 11. |
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 12. |
|
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 13. |
|
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 14. |
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 15. |
|
|
53 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F - 1 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
- 1 -
General
Company Background. Barrett Business Services, Inc. (“BBSI,” the “Company,” “our” or “we”), is a leading provider of business management solutions for small and mid-sized companies. The Company has developed a management platform that integrates a knowledge-based approach from the management consulting industry with tools from the human resource outsourcing industry. This platform, through the effective leveraging of human capital, helps our business owner clients run their businesses more effectively. We believe this platform, delivered through a decentralized organizational structure, differentiates BBSI from our competitors. BBSI was incorporated in Maryland in 1965.
Certain statements below contain forward-looking information that is subject to risks and uncertainties. See “Forward-Looking Information” in Item 7 of Part II of this report and “Risk Factors” in Item 1A of Part I of this report.
Business Strategy. Our strategy is to align local operations teams with the mission of small and mid-sized business owners, driving value to their business. To do so, BBSI:
|
|
• |
partners with business owners to leverage their investment in human capital through a high-touch, results-oriented approach; |
|
|
• |
brings predictability to each client organization through a three-tiered management platform; and |
|
|
• |
enables business owners to focus on their core business by reducing organizational complexity and maximizing productivity. |
Business Organization. We operate a decentralized delivery model using operationally-focused business teams, typically located within 50 miles of our client companies. These teams are led by senior level business generalists and comprise senior level professionals with expertise in human resources, organizational development, risk mitigation and workplace safety and various types of administration, including payroll. These teams are responsible for growth of their operations, and for providing strategic leadership, guidance and expert consultation to our client companies. The decentralized structure fosters autonomous decision-making in which business teams deliver plans that closely align with the objectives of each business owner client. This structure also provides a means of incubating talent to support increased growth and capacity. We support clients with employees located in 20 states and the District of Columbia through a network of 57 branch locations in California, Oregon, Utah, Washington, Idaho, Arizona, Colorado, Maryland, North Carolina, Delaware, Nevada, Pennsylvania and Virginia. We also have several smaller recruiting locations in our general market areas, which are under the direction of a branch office.
BBSI believes that making significant investments in the best talent available allows us to leverage the value of this investment many times over. We motivate our management employees through a compensation package that includes a competitive base salary and the opportunity for profit sharing. At the branch level, profit sharing is in direct correlation to client performance, reinforcing a culture focused on achievement of client goals.
- 2 -
Services Overview. BBSI’s core purpose is to advocate for business owners, particularly in the small and mid-sized business segment. Our evolution from an entrepreneurially run company to a professionally managed organization has helped to form our view that all businesses experience inflection points at key stages of growth. The insights gained through our own growth, along with the trends we see in working with more than 4,900 companies each day, define our approach to guiding business owners through the challenges associated with being an employer. BBSI’s business teams align with each business owner client through a structured three-tiered progression. In doing so, business teams focus on the objectives of each business owner and deliver planning, guidance and resources in support of those objectives.
Tier 1: Tactical Alignment
The first stage focuses on the mutual setting of expectations and is essential to a successful client relationship. It begins with a process of assessment and discovery in which the business owner’s business objectives, attitudes, and culture are aligned with BBSI’s processes, controls and culture. This stage includes an implementation process, which addresses the administrative components of employment.
Tier 2: Dynamic Relationship
The second stage of the relationship emphasizes organizational development as a means of achieving each client’s business objectives. There is a focus on process improvement, development of best practices, supervisor training and leadership development.
Tier 3: Strategic Counsel
With an emphasis on advocacy on behalf of the business owner, the third stage of the relationship is more strategic and forward-looking with a goal of cultivating an environment in which all efforts are directed by the mission and long-term objectives of the business owner.
In addition to serving as a resource and guide, BBSI has the ability to provide workers’ compensation coverage as a means of meeting statutory requirements and protecting our clients from employment-related injury claims. Through our internal claims managers and our third-party administrators, we provide claims management services for our clients. We work aggressively to manage and reduce job injury claims, identify fraudulent claims and structure optimal work programs, including modified duty.
Categories of Services
We report financial results in two categories of services: Professional Employer Services (“PEO”) and Staffing. During 2016, we supported in excess of 4,900 PEO clients and approximately 171,000 employees. This compares to more than 4,100 PEO clients and approximately 151,000 employees during 2015. See Item 7 of this Report for information regarding the percentages of total net revenues provided by our PEO and staffing services for each of the last three fiscal years, and our consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this Report for information regarding revenues, net income and total assets in our single reportable segment.
PEO. We enter into a client services agreement to establish a co-employment relationship with each client company, assuming responsibility for payroll, payroll taxes, workers’ compensation coverage and certain other administrative functions for the client’s existing workforce. The client maintains physical care, custody and control of their workforce, including the authority to hire and terminate employees.
Staffing and Recruiting. Our staffing services include on-demand or short-term staffing assignments, contract staffing, direct placement, and long-term or indefinite-term on-site
- 3 -
management. On-site management employees are BBSI management employees who are based on the client-site and whose jobs are to assist BBSI staffing employees. Our recruiting experts maintain a deep network of professionals from which we source candidates. Through an assessment process, we gain an understanding of the short-and long-term needs of our clients, allowing us to identify and source the right talent for each position. We then conduct a rigorous screening process to help ensure a successful hire.
Clients and Client Contracts
Our business is typically characterized by long-term relationships that result in recurring revenue. The terms and conditions applicable to our client relationships are set forth in a client services agreement, which typically provides for an initial term of one year with renewal for additional one-year periods, but generally permits cancellation by either party upon 30 days’ written notice. In addition, we may terminate the agreement at any time for specified breach of contract, including nonpayment or failure to follow our workplace safety recommendations. Our annual client retention rate is in excess of 90%.
The client services agreement also provides for indemnification by the client against losses arising out of any default by the client under the agreement, including failure to comply with any employment-related, health and safety, or immigration laws or regulations. Our client service agreement requires that clients enter into a co-employment arrangement and maintain comprehensive liability coverage in the amount of $1.0 million for acts of their employees. It is nevertheless possible that claims not satisfied through indemnification or insurance may be asserted against us, which could adversely affect our results of operations.
We have client services agreements with a diverse array of customers, including electronics manufacturers, various light-manufacturing industries, agriculture-based companies, transportation and shipping enterprises, food processors, telecommunications companies, public utilities, general contractors in various construction-related fields, and professional services firms. None of our clients individually represented more than 1% of our total revenues in 2016.
Market Opportunity
As a company that aligns with the mission of business owners by providing resources and guidance to small and mid-size businesses, BBSI believes its growth is driven by the desire of business owners to focus on mission-critical functions, reduce complexity associated with the employment function, mitigate costs and maximize their investment in human capital. Our integrated management platform has enabled us to capitalize on these needs within the small to mid-size business sector.
The small and mid‑sized business segment is particularly attractive because:
|
|
• |
it is large, continues to grow and remains underserved by professional services companies; |
|
|
• |
it typically has fewer in-house resources than larger businesses and, as a result, is generally more dependent on external resources; |
|
|
• |
we generally experience a relatively high client retention rate and lower client acquisition costs within this market segment; and |
- 4 -
|
|
• |
we have found that small to mid-sized businesses are responsive to quality of service, ease-of-use, and responsiveness to clients' needs when selecting a PEO or staffing services provider. |
Competition
The business environment in which we operate is characterized by intense competition and fragmentation. BBSI is not aware of reliable statistics regarding the number of its competitors, but certain large, well-known companies typically compete with us in the same markets and also have greater financial and marketing resources than we do, including Automatic Data Processing, Inc., ManpowerGroup, Inc., Kelly Services, Inc., Insperity, Inc., TriNet Group, Inc., Robert Half International Inc. and Paychex, Inc. We face additional competition from regional providers and we may in the future also face competition from new entrants to the field, including other staffing services companies, payroll processing companies and insurance companies. The principal competitive factors in the business environment in which we operate are price and level of service.
We believe that our growth is attributable to our ability to provide small and mid-sized companies with the resources and knowledge base of a large employer delivered through a local operations team. Our level of integration with each client business provides us an additional competitive advantage.
Growth Strategy
We believe our clients are our best advocates and powerful drivers of referral-based growth. In each market, operations teams provide expertise, consultation and support to our clients, driving growth and supporting retention. We anticipate that by adding business teams to existing branches, we can achieve incremental growth in those markets, driven by our reputation and by client referrals. While in most markets business development efforts are led by area managers, in some markets our sales efforts are further supported by Business Development Managers.
Our business growth has three primary sources: referrals from existing clients, direct business-to-business sales efforts by our area managers and an extensive referral network. Partners in our referral network include insurance brokers, financial advisors, attorneys, CPA’s, and other business professionals who can facilitate an introduction to prospective clients. These referral partners facilitate introductions to business owners on our behalf, typically in exchange for a fee equal to a small percentage of payroll.
We see two key drivers to our growth:
|
|
• |
Increase market share in existing markets. We seek to support, strengthen and expand branch office operations through the ongoing development of business teams. We believe that strengthening and expanding the operations of each location is an efficient and effective means of increasing market share in the geographic areas in which we do business, and that our business teams serve a dual purpose: 1) Delivering high-quality service to our clients, thereby supporting client business growth and retention, and driving client referrals, and 2) Incubating talent at the branch level to support expansion into new markets. |
|
|
• |
Penetrate new markets. We intend to open additional branch offices in new geographic markets as opportunities arise. We have developed a strategic approach to geographic expansion, which will serve as a guide for determining if and when to enter new markets. |
- 5 -
|
|
We believe our decentralized organizational model built on teams of senior-level professionals allows us to incubate talent to support our expansion efforts. |
Workers’ Compensation
Through our client services agreement, we have the ability to provide workers’ compensation coverage to our clients. We provide this coverage through a variety of methods, all of which are subject to rigorous underwriting to assess financial stability, risk factors and cultural alignment related to safety and the client’s desire to improve their operations. In providing this coverage, we are responsible for complying with applicable statutory requirements for workers' compensation coverage.
Risk mitigation is also an important contributor to our principal goal of helping business owners operate their business more efficiently. It is in the mutual interests of the client and BBSI to commit to workplace safety and risk mitigation.
Elements of Workers' Compensation System. State law (and for certain types of employees, federal law) generally mandates that an employer reimburse its employees for the costs of medical care and other specified benefits for injuries or illnesses, including catastrophic injuries and fatalities, incurred in the course and scope of employment. Most states require employers to maintain workers' compensation insurance or otherwise demonstrate financial responsibility to meet workers' compensation obligations to employees. The benefits payable for various categories of claims are determined by state regulation and vary with the severity and nature of the injury or illness and other specified factors. In return for this guaranteed protection, workers' compensation is an exclusive remedy and employees are generally precluded from seeking other damages from their employer for workplace injuries. In many states, employers who meet certain financial and other requirements are permitted to self-insure.
Insurance Coverage for Workers' Compensation. The Company is a self-insured employer with respect to workers' compensation coverage for all of its employees (including employees co-employed through our client service agreements) working in Colorado, Maryland and Oregon. In the state of Washington, state law allows only the Company's staffing services and internal management employees to be covered under the Company's self-insured workers' compensation program.
Regulations governing self-insured employers in each jurisdiction typically require the employer to maintain surety bonds, surety deposits of government securities, letters of credit or other financial instruments to cover workers' claims in the event the employer is unable to pay for such claims.
BBSI was self-insured as to worker’s compensation claims in California from 1995 until December 31, 2014. Effective January 1, 2015, the Company ceased maintaining a certificate to self-insure in the state of California, and it now maintains individual policies with Chubb Limited (“Chubb”, formerly ACE Group) for all clients in California, along with clients in Delaware, Virginia, Pennsylvania, North Carolina, New Jersey, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia. See “Regulatory Changes in California” below for further discussion of these developments in California.
To manage our financial exposure to catastrophic injuries and fatalities, we maintain excess workers' compensation insurance coverage. Our wholly owned, fully licensed captive insurance company incorporated in Arizona, Associated Insurance Company for Excess (“AICE”), provides excess workers' compensation coverage up to $5.0 million per occurrence, except in Maryland and Colorado, where our retention per occurrence is $1.0 million and $2.0
- 6 -
million, respectively. AICE maintains excess workers’ compensation insurance coverage with Chubb between $5.0 million and $15.0 million per occurrence, except in Maryland, where coverage with Chubb is between $1.0 million and $25.0 million per occurrence, and in Colorado, where the coverage with Chubb is between $2.0 million and statutory limits per occurrence.
Overall, this approach results in a per occurrence retention on a consolidated basis of $5.0 million for most claims. In light of the higher per occurrence retention, we may incur higher workers' compensation costs and a corresponding negative effect on our operating results.
AICE provides us with access to an alternative mechanism for excess insurance coverage, as well as certain income tax benefits arising from the ability to accelerate the tax deduction of certain accruals for workers' compensation claims.
The Company also operates a wholly owned insurance company, Ecole Insurance Company (“Ecole”). Ecole is a fully licensed insurance company holding a certificate of authority from the Arizona Department of Insurance. Ecole provides workers’ compensation coverage to the Company’s employees working in Arizona, Utah and Nevada. The Company maintains additional reinsurance coverage for Ecole with Chubb between $5.0 million and $15.0 million per occurrence.
Claims Management. As a result of our status as a self-insured employer in four states and our retention arrangements, our workers' compensation expense is tied directly to the incidence and severity of covered workplace injuries. We seek to contain our workers' compensation costs through an aggressive approach to claims management. We use managed-care systems to reduce medical costs and keep time-loss costs to a minimum by assigning injured workers, whenever possible, to short-term assignments which accommodate the workers' physical limitations. We believe that these assignments minimize both time actually lost from work and covered time-loss costs. We employ internal, professionally licensed claims adjusters and engage third-party claims administrators ("TPAs") to provide the primary claims management expertise. Typical claims management procedures include performing thorough and prompt on-site investigations of claims filed by employees, working with physicians to encourage efficient medical management of cases, denying questionable claims and attempting to negotiate early settlements to eliminate future adverse development of claims costs. We also maintain a corporate-wide pre-employment drug screening program and a post-injury drug test program. We believe our claims management program has resulted in a reduction in the frequency of fraudulent claims and in accidents in which the use of illicit drugs appears to have been a contributing factor.
Regulatory Changes in California. Effective January 1, 2015, we ceased maintaining a certificate to self-insure in the state of California as mandated by California law adopted in September 2012. To address the law’s prohibition of self-insuring for workers’ compensation, in February 2014 BBSI entered into an arrangement typically known as a fronted insurance program with Chubb. The arrangement with Chubb provides BBSI a licensed, admitted insurance carrier to issue policies on behalf of BBSI. The risk of loss up to the first $5.0 million per claim is retained by BBSI through a reinsurance agreement. Chubb assumes credit risk should BBSI be unable to satisfy its indemnification obligations. In addition, Chubb continues to be BBSI’s carrier for costs in excess of $5.0 million per claim. We transitioned all California-based clients and their employees to Chubb policies prior to December 31, 2014.
Components of Our Workers’ Compensation Costs. The costs associated with our workers' compensation program include case reserves for reported claims, an additional expense provision for potential future increases in the cost to finally resolve open injury claims (known as
- 7 -
"adverse loss development") and claims incurred in prior periods but not reported (together with adverse loss development, "IBNR"), fees payable to our TPAs, additional claims administration expenses, administrative fees payable to state workers' compensation regulatory agencies, legal fees, medical cost containment (“MCC”) fees, business referral fees, premiums for excess workers' compensation insurance, premiums for the fronted insurance program through Chubb, and costs associated with operating our two wholly owned, fully licensed insurance companies, AICE and Ecole. The state assessments are typically based on payroll amounts and, to a limited extent, the amount of permanent disability awards during the previous year. Excess insurance premiums are also based in part on the size and risk profile of our payroll and loss experience.
Workers' Compensation Claims Experience and Reserves
We recognize our liability for the ultimate payment of incurred claims and claims adjustment expenses by establishing a reserve which represents our estimates of future amounts necessary to pay claims and related expenses with respect to work place injuries that have occurred. When a claim involving a probable loss is reported, our internal claims management personnel or our TPA establishes a case reserve for the estimated amount of ultimate loss. The estimate reflects a judgment based on established case reserving practices and the experience and knowledge of our claims management staff and the TPA regarding the nature and expected amount of the claim, as well as the estimated expenses of settling the claim, including legal and other fees and expenses of claims administration. The adequacy of such case reserves in part depends on the professional judgment of both our claims management staff and our TPA to properly and comprehensively evaluate the economic consequences of each claim. Our reserves include an additional component for IBNR, which includes estimates for both future adverse loss development in excess of initial case reserves on open claims and incurred but not reported claims based on actuarial estimates provided by the Company’s independent actuary. Our reserves also include an accrual for MCC fees. Our reserves do not include an estimated provision for the incidence of unknown or unreported catastrophic claims.
As part of the case reserving process, historical data is reviewed and consideration is given to the anticipated effect of various factors, including known and anticipated legal developments, inflation and economic conditions. Case reserve amounts are based on management's estimates, and as other data becomes available, these estimates are revised, which may result in increases or decreases in existing case reserves. Management's internal accrual process for workers' compensation expense is based upon the immediate recognition of an expense and the related liability at the time a claim occurs; the value ascribed to the expense and liability is based upon our internal claims management and the TPAs’ estimate of ultimate claim cost coupled with a provision for estimated future development based upon an actuarial review performed by our independent actuary. We believe our total accrued workers' compensation claims liabilities at December 31, 2016 are adequate. It is possible, however, that our actual future workers' compensation obligations may exceed the amount of our accrued liabilities, with a corresponding negative effect on future earnings, due to such factors as unanticipated adverse loss development of known claims and, to a much lesser extent, of claims incurred but not reported.
We maintain clear guidelines for our area managers and risk management consultants, directly tying their continued employment to their diligence in understanding and addressing the risks of accident or injury associated with the industries in which client companies operate and in monitoring clients’ compliance with workplace safety requirements.
- 8 -
Employees and Employee Benefits
At December 31, 2016, we had 115,746 total employees, including 9,628 staffing services employees, 105,461 employees under our client service agreements, 653 managerial, sales and administrative employees (together, “management employees”), and 4 executive officers. The number of employees at any given time may vary significantly due to business conditions at customer or client companies. We believe our employee relations are good.
We offer various qualified employee benefit plans to our employees, including those employees for whom we are the administrative employer in a co-employment arrangement who so elect. Employees covered under a PEO arrangement may participate in our 401(k) plan at the sole discretion of the PEO client. All qualified staffing and management employee benefit plans include our 401(k) plan to which employees may enroll upon reaching 21 years of age and completing 1,000 hours of service in a 12 consecutive month period. We make matching contributions to the 401(k) plan under a safe harbor provision, which are immediately 100% vested. We match 100% of contributions by management and staffing employees up to 3% of each participating employee's annual compensation and 50% of the employee's contributions up to an additional 2% of annual compensation. We may also make discretionary contributions to the 401(k) plan, which vest over six years and are subject to certain legal limits, at the sole discretion of our Board of Directors.
We also offer a cafeteria plan under Section 125 of the Internal Revenue Code, and group health, life insurance and disability insurance plans to qualified staffing and management employees. Generally, qualified employee benefit plans are subject to provisions of both the Internal Revenue Code and the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 ("ERISA"). In order to qualify for favorable tax treatment under the Internal Revenue Code, qualified plans must be established and maintained by an employer for the exclusive benefit of its employees.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (collectively, the “Acts”) subject us to potential penalties unless we offer to our employees minimum essential healthcare coverage that is affordable. Because our PEO clients are considered to be the sole employer in the application of any rule or law included within the scope of the Acts, we do not offer health care coverage to the employees of our PEO clients. However, in order to comply with the employer mandate provision of the Acts, we offer health care coverage to all eligible staffing employees and management employees eligible for coverage under the Acts.
Regulatory and Legislative Issues
We are subject to the laws and regulations of the jurisdictions within which we operate, including those governing self-insured employers under the workers' compensation systems in Oregon, Maryland, and Colorado, as well as in Washington for staffing and management employees. We are also subject to laws and regulations governing our two wholly owned, fully licensed insurance companies in Arizona. While the specific laws and regulations vary among these jurisdictions, they typically require some form of licensing and often have statutory requirements for workplace safety and notice of change in obligation of workers’ compensation coverage in the event of contract termination. Although compliance with these requirements imposes some additional financial risk, particularly with respect to those clients who breach their payment obligation to us, such compliance has not had a material adverse effect on our business to date.
Our operations are affected by numerous federal and state laws relating to labor, tax and employment matters. Through our client services agreement, we assume certain obligations
- 9 -
and responsibilities as the administrative employer under federal and state laws. Since many of these federal and state laws were enacted prior to the development of nontraditional employment relationships, such as professional employer, temporary employment, and outsourcing arrangements, many of these laws do not specifically address the obligations and responsibilities of nontraditional employers. In addition, the definition of "employer" under these laws is not uniform.
As an employer, we are subject to all federal statutes and regulations governing our employer-employee relationships. Subject to the discussion of risk factors below, we believe that our operations are in compliance in all material respects with applicable federal statutes and regulations.
Additional Information
Our filings with the SEC, including our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, periodic reports on Form 8-K and amendments to these reports, are accessible free of charge at our website at http://www.barrettbusiness.com as soon as reasonably practicable after they are electronically filed with the SEC. By making this reference to our website, we do not intend to incorporate into this report any information contained in the website. The website should not be considered part of this report.
Materials that the Company files with the SEC may be read and copied at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE., Washington, DC 20549. Information on the operation of the Public Reference Room may be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC also maintains a website at http://www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers with publicly traded securities, including the Company.
In addition to other information contained in this report, the following risk factors should be considered carefully in evaluating our business.
Risks Related to our Consolidated Financial Statements and Internal Controls
The restatement of our previously issued consolidated financial statements may expose us to additional risks that could materially and adversely affect our financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
We have incurred significant expenses, including audit, legal, consulting and other professional fees, in connection with the restatement of our previously issued financial statements described in “Note 2. Restatement of Previously Issued Financial Statements” to the consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of the 2015 Form 10-K. We cannot predict what losses we may incur in litigation matters, regulatory enforcement actions and contingencies related to our obligations under the federal and state securities laws, in connection with the restatement of previously issued financial statements or in other legal proceedings.
As described in more detail in “Item 3. Legal Proceedings” and in “Note 12. Litigation” to the consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this report, a lawsuit purporting to be a class action on behalf of all of BBSI’s stockholders was filed in the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington against BBSI and BBSI’s Chief Executive Officer and former Chief Financial Officer. The complaint alleged violations of the
- 10 -
federal securities laws based on claims arising from declines in the market price for our common stock following announcement of a charge for increased workers’ compensation reserves expense in October 2014 and the events reported in March 2016 that resulted in the restatement of our previously issued financial statements.
On October 26, 2016, the parties entered into a Stipulation and Agreement of Settlement dated as of October 26, 2016 (the “Settlement”), to settle the litigation. The Settlement is intended to fully, finally and forever compromise, settle, release, resolve, and dismiss with prejudice the purported class action and all claims asserted therein against the named defendants. In the Settlement, the defendants denied all allegations of wrongdoing and the plaintiffs did not concede any infirmities in their positions. The Settlement called for the payment in cash of $12.0 million (the “Settlement Fund”) into escrow by November 29, 2016. Of this amount, approximately $8.7 million was paid by BBSI’s insurance carriers and approximately $3.3 million was paid by BBSI. The Settlement was approved by the court on February 22, 2017. The fees of counsel for the plaintiffs will be paid out of the Settlement Fund following approval by the court.
As also discussed in Item 3 and Note 12, a shareholder derivative lawsuit was filed in June 2015 against BBSI and certain of its officers and directors in the Circuit Court for Baltimore City, Maryland. The complaint alleges breaches of fiduciary duty, unjust enrichment and other violations of law and seeks recovery of various damages, including costs and expenses incurred in connection with the announcements of the workers’ compensation reserve charge in October 2014, as well as the proceeds of sales of stock by certain of BBSI’s officers and directors during 2013 and 2014.
In addition, BBSI received a subpoena from the San Francisco office of the Division of Enforcement of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) in April 2016 in connection with the SEC’s inquiry into reported errors in our financial statements. The Company previously received a subpoena from the SEC in May 2015 in connection with the SEC’s investigation of the Company’s accounting policies with regard to its workers’ compensation reserves. BBSI was also advised by the United States Department of Justice in mid-June 2016 that it has commenced an investigation. The Company is cooperating fully with the investigations. See Item 3 and Note 12 for additional information. Potential civil or criminal proceedings arising out of the investigations could result in the imposition of substantial fines and other penalties on the Company, including those related to failure to keep accurate books and records.
The legal proceedings described above, if decided adversely to us or to our directors or officers, could result in additional significant monetary damages or penalties or reputational harm, and also have involved and likely will continue to involve significant defense and other costs. We have entered into indemnification agreements with each of our directors and certain of our officers, and our corporate charter requires us to indemnify each of our officers and directors against all liabilities, losses, judgments, penalties, fines, settlements and reasonable expenses arising out of their actions in such capacities to the fullest extent permitted by Maryland law. We have exhausted the coverage limits of certain insurance policies, primarily due to the Settlement described above. Our insurance coverage may not cover additional claims that have been or may be brought against us. As a result, we may be exposed to substantial uninsured liabilities, including pursuant to our indemnification obligations, which could adversely affect our business, prospects, results of operations and financial condition. Management is unable to estimate the probability, or the potential range, of loss arising from the legal actions described above beyond that described in the Settlement. The Company has not reserved any amount in respect of these matters in its consolidated financial statements. These
- 11 -
lawsuits and regulatory proceedings may also continue to divert the efforts and attention of the Company’s management from business operations.
There are various other claims, lawsuits and pending actions against us from time to time. While we cannot predict what losses we may incur from these other legal proceedings or contingencies, it is our opinion that the ultimate resolution of these other matters will not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position. However, the resolution of certain of these matters could be material to our operating results for any particular period, depending on the level of income for such period. We can make no assurances that we will ultimately be successful in our defense of any of these other matters.
We face risks to our reputation and investor confidence arising from material weaknesses in our internal control environment over financial reporting.
Management has identified material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016. Our chief executive officer and chief financial officer have also concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of December 31, 2016. Although management has formulated and is implementing a plan to remediate these material weaknesses, we expect implementation to continue to be time consuming and expensive, and the remedial actions we take may prove to be ineffective or inadequate. As a result, the Company may continue to be exposed to risk of misstatements in its financial statements. In such circumstances, investors and other users of BBSI’s financial statements may lose confidence in the reliability of our financial information, and BBSI could be in breach of certain representations and covenants in its credit agreement with its primary bank (the “Credit Agreement”) or be obligated to incur additional costs to improve our internal controls. Any failure or inability to remediate the material weaknesses in a timely and effective manner could also adversely affect our reputation and business prospects. See “Item 9A. Controls and Procedures” in Part II of this report for a more detailed description of the material weaknesses identified by management and plans to remediate these material weaknesses.
Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry
Our workers' compensation claims reserves may be inadequate to cover our ultimate liability for workers' compensation costs.
We maintain reserves (recorded as accrued liabilities on our balance sheet) to cover our estimated liabilities for workers' compensation claims, whether arising in connection with our fronted insurance arrangement with Chubb in California, Delaware, Virginia, Pennsylvania, North Carolina, New Jersey, West Virginia and the District of Columbia, our self-insured status in Oregon, Maryland, Colorado and Washington, or the business of our insurance subsidiary Ecole in Arizona, Utah and Nevada. The Company maintains excess workers’ compensation insurance coverage with Chubb through our AICE subsidiary, but it remains responsible for costs below amounts of its excess coverage in each state. The determination of our reserves is based upon estimates arising out of evaluation of a number of factors, including current and historical claims activity, claims payment patterns, medical cost trends, and additional adverse loss development of existing claims. Our reserves include an additional component for both estimated future adverse loss development in excess of initial case reserves on open claims and for incurred but not reported claims that represents the actuarial estimates provided by the Company’s independent actuary. Our reserves also include an estimate of future legal and MCC fees but do not include an estimated provision for the incidence of unknown catastrophic claims. Reserves may be affected by both internal and external events, including changes in claims handling practices, modifications in reserve estimation procedures, trends in the litigation and
- 12 -
settlement of pending claims and legislative changes. Reserves are adjusted from time to time to reflect new claims, claim development, or systemic changes, and such adjustments are reflected in the financial results for the periods in which the reserves are changed. As a result of the various estimates involved and other factors, our workers’ compensation reserves do not represent an exact calculation of liability. Moreover, because of the uncertainties that surround estimating workers' compensation loss reserves, our reserves may prove to be inadequate. If our reserves are insufficient to cover our actual losses, we will be required to increase our reserves and incur charges to our earnings that could be material to our results of operations and financial condition. See “Item 1. Business--Workers’ Compensation” and “Note 5. Workers’ Compensation Claims” to the consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this report for additional information.
Our consolidated retention for workers' compensation claims is $5.0 million per occurrence under our insurance arrangement with Chubb in the majority of states in which we operate.
We maintain our consolidated retention at $5.0 million per occurrence, except in Colorado and Maryland where our retention is at $2.0 million and $1.0 million per occurrence, respectively, due to regulatory requirements. The Company maintains its excess workers’ compensation insurance coverage with Chubb through our AICE subsidiary. Additionally, Ecole’s retention is at $5.0 million per occurrence for coverage in Arizona, Nevada and Utah. Thus, the Company has financial risk for most workers' compensation claims under $5.0 million on a per occurrence basis. This level of per occurrence retention may result in higher workers’ compensation costs to us with a corresponding negative effect on our operating results and financial condition.
Adverse developments in the market for excess workers' compensation insurance could lead to increases in our costs.
To manage our financial exposure in the event of catastrophic injuries or fatalities, we maintain excess workers' compensation insurance. Changes in the market for excess workers' compensation insurance may lead to limited availability of such coverage, additional increases in our insurance costs or further increases in the amount for which we have financial risk, any of which may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Our ability to continue our business operations under our present service model is dependent on maintaining workers' compensation insurance coverage.
Our arrangement with Chubb to provide workers’ compensation coverage to BBSI’s PEO clients in California, Delaware, Virginia, Pennsylvania, North Carolina, New Jersey, West Virginia and the District of Columbia extends through February 1, 2018, with the possibility of additional annual renewals. If Chubb is unwilling or unable to renew our arrangement in the future, we would need to seek alternative coverage. If replacement coverage were unavailable or available only on significantly less favorable terms, our business and results of operations would be materially adversely affected.
Failure to manage the severity and frequency of workplace injuries will increase our workers’ compensation expenses.
Significant increases in the relative frequency or severity of workplace injuries due to failures to accurately assess potential risks or assure implementation of effective safety
- 13 -
measures by our clients may result in increased workers’ compensation claims expenses, with a corresponding negative effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
We may be unable to draw on our revolving credit facility in the future.
As discussed in more detail in “Note 6. Revolving Credit Facility and Long-Term Debt” to the consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this report, our Credit Agreement with our principal bank, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association (the “Bank”), which expires July 1, 2018, provides for a revolving credit facility with a borrowing capacity of up to $25.0 million at December 31, 2016, to be used to finance working capital. There was no outstanding balance at that date. The Credit Agreement includes a standby letter of credit agreement providing for a total of approximately $5.0 million in cash-secured letters of credit and also a mortgage loan with a balance of approximately $4.6 million secured by our company office building in Vancouver, Washington.
If our business does not perform as expected, including if we generate less revenue than anticipated from our operations or encounter significant unexpected costs, we may fail to comply with the financial covenants under our credit facilities. If we do not comply with our financial covenants and we do not obtain a waiver or amendment from the Bank, the Bank may elect to cause all amounts owed to become immediately due and payable. In that event, we would seek to establish a replacement credit facility with one or more other lenders, including lenders with which we have an existing relationship, potentially on less desirable terms. There can be no guarantee that replacement financing would be available at commercially reasonable terms, if at all.
Our business is subject to risks associated with geographic market concentration.
Our California operations accounted for approximately 78% of our total revenues in 2016. As a result of the current importance of our California operations and anticipated continued growth from these operations, our profitability over the next several years is expected to be largely dependent on economic and regulatory conditions in California. If California experiences an economic downturn, or if the regulatory environment changes in a way that adversely affects our ability to do business or limits our competitive advantages, our profitability and growth prospects may be materially adversely affected.
In order to continue to grow revenues at or near current rates, we are dependent on retaining current clients and attracting new clients.
The Company has experienced significant growth in recent years. Revenues increased 13.5% in 2016 and 16.4% in 2015. There can be no assurance that we will continue to grow revenues at or near current rates of growth. Maintaining rates of growth at these levels becomes increasingly difficult as the size of the Company increases. Efforts to achieve business growth intensifies pressure on retaining current clients and attracting increasing numbers of new clients.
- 14 -
Economic conditions, particularly in California, may impact our ability to attract new clients and cause our existing clients to reduce staffing levels or cease operations.
Weak economic conditions typically have a negative impact on small-and mid-sized businesses, which make up the majority of our clients. In turn, these businesses could cut costs, including trimming employees from their payrolls, or closing locations or ceasing operations altogether. If weak economic conditions were to develop, these forces may result in decreased revenues due both to the downsizing of our current clients and increased difficulties in attracting new clients in a poor economic environment. In addition, weak economic conditions may also result in additional bad debt expense to the extent that existing clients cease operations.
Our business is subject to risks associated with healthcare reforms.
In March 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (collectively, the “Acts”) were signed into U.S. law. The Acts represent comprehensive U.S. healthcare reform legislation that, in addition to other provisions, subjects us to potential penalties unless we offer our employees minimum essential healthcare coverage that is affordable. In order to comply with the employer mandate provision of the Acts, we offer health care coverage to all temporary and permanent employees eligible for coverage under the Acts other than employees of our PEO clients, which are responsible for providing required health care coverage to their employees. Designating employees as eligible is complex, and is subject to challenge by employees and the Internal Revenue Service. While we believe we have properly identified eligible employees, a later determination that we failed to offer the required health coverage to eligible employees could result in penalties that may materially harm our business. We cannot be certain that compliant insurance coverage will remain available to us on reasonable terms, and we could face additional risks arising from future changes to or repeal of the Acts or changed interpretations of our obligations under the Acts. There can be no assurance that we will be able to recover all related costs through increased pricing to our customers or that such costs will be recovered in the period in which costs are incurred, and the net financial impact on our results of operations could be significant.
If we are unable to maintain our brand image and corporate reputation, our business may suffer.
Our success depends in part on our ability to maintain our reputation for providing excellent service to our customers. Service quality issues, actual or perceived, even when false or unfounded, could tarnish the image of our brand and may cause customers to use other companies. Also, adverse publicity surrounding labor relations, data breaches, SEC investigations, securities class actions and the like, could negatively affect our overall reputation. Damage to our reputation could reduce demand for our services and thus have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our staffing business is vulnerable to economic fluctuations.
Demand for our staffing services is sensitive to changes in the level of economic activity in the regions in which we do business. As economic activity slows down, companies often reduce their use of temporary employees before undertaking layoffs of permanent staff, resulting in decreased demand for staffing services. During strong economic periods, on the other hand, we often experience shortages of qualified employees to meet customer needs.
- 15 -
Because we assume the obligation to make wage, tax and regulatory payments in respect of some employees, we are exposed to client credit risks.
We generally assume credit risk associated with our clients’ employee payroll obligations, including liability for payment of salaries and wages (including payroll taxes), as well as group health and retirement benefits. These obligations are fixed whether or not the client makes payments to us as required by our services agreement. We attempt to mitigate this risk by invoicing our clients at the end of their specific payroll processing cycle. We also carefully monitor the timeliness of our clients' payments and impose strict credit standards on our customers. If we fail to successfully manage our credit risk, our results of operations and financial condition could be materially and adversely affected.
Increases in unemployment claims could raise our state and federal unemployment tax rates which we may not be able to pass on to our customers.
During weak economic conditions in our markets, the level of unemployment claims tends to rise as a result of employee layoffs at our clients and lack of work in our temporary staffing pool. The rise in unemployment claims often results in higher state and federal unemployment tax rates which in most instances cannot be concurrently passed on to our customers either due to existing client services agreements or competitive pricing pressures. Increases in our state and federal unemployment tax rates could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, particularly in the early part of the calendar year when payroll tax rates are at or near their maximum.
If we are determined not to be an “employer” under certain laws and regulations, our clients may stop using our services, and we may be subject to additional liabilities.
We are the administrative employer in our co-employment relationships under the various laws and regulations of the Internal Revenue Service and the U.S. Department of Labor. If we are determined not to be the administrative employer under such laws and regulations and are therefore unable to assume our clients’ obligations for employment and other taxes, our clients may be held jointly and severally liable for payment of such taxes. Some clients or prospective clients may view such potential liability as an unacceptable risk, discouraging current clients from continuing a relationship with us or prospective clients from entering into a new relationship with us. Any determination that we are not the administrative employer for purposes of ERISA could also adversely affect our cafeteria benefits plan operated under Section 125 of the Internal Revenue Code and result in liabilities to us under the plan.
We may be exposed to employment‑related claims and costs and periodic litigation that could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
We either co-employ employees in connection with our client services agreements or place our employees in our customers' workplace in connection with our staffing business. As such, we are subject to a number of risks inherent to our status as the administrative employer, including without limitation:
|
|
• |
claims of misconduct or negligence on the part of our employees, discrimination or harassment claims against our employees, or claims by our employees of discrimination or harassment by our clients; |
|
|
• |
immigration-related claims; |
- 16 -
|
|
• |
claims relating to violations of wage, hour and other workplace regulations; |
|
|
• |
claims relating to employee benefits, entitlements to employee benefits, or errors in the calculation or administration of such benefits; and |
|
|
• |
possible claims relating to misuse of customer confidential information, misappropriation of assets or other similar claims. |
If we experience significant incidents involving any of the above-described risk areas we could face substantial out-of-pocket losses, fines or negative publicity. In addition, such claims may give rise to litigation, which may be time consuming, distracting and costly, and could have a material adverse effect on our business. With respect to claims involving our co-employer relationships, although our client services agreement provides that the client will indemnify us for any liability attributable to the conduct of the client or its employees, we may not be able to enforce such contractual indemnification, or the client may not have sufficient assets to satisfy its obligations to us. An increase in employment-related claims against us may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We are dependent upon technology services and if we experience damage, service interruptions or failures in our computer and telecommunications systems, our client relationships and our ability to attract new clients may be adversely affected.
We rely extensively on our computer systems to manage our branch network, perform employment-related services, accounting and reporting, and summarize and analyze our financial results. Our systems are subject to damage or interruption from telecommunications failures, power-related outages, computer viruses and malicious attacks, security breaches and catastrophic events. If our systems are damaged or fail to function properly, we may incur substantial costs to repair or replace them, experience loss of critical data and interruptions or delays in our ability to manage our operations, and encounter a loss of client confidence. In addition, our clients’ businesses may be adversely affected by any system or equipment failure or breach we experience. As a result, our relationships with our clients may be impaired, we may lose clients, our ability to attract new clients may be adversely affected and we could be exposed to contractual liability. We may invest in upgrades or replacements to our existing systems or additional security measures, each of which can involve substantial costs and risks relating to installation and implementation.
We depend on third-party software in order to provide our services and support our operations.
Significant portions of our services and operations rely on software that is licensed from third-party vendors. The fees associated with these license agreements could increase in future periods resulting in increased operating expenses. If there are significant changes to the terms and conditions of our license agreements, or if we are unable to renew these license agreements, we may be required to make changes to our vendors or information technology systems. These changes may impact the services we provide to our clients or the processes we have in place to support our operations, which could have an adverse effect on our business.
- 17 -
If our efforts to protect the security of personal information about our employees and clients are unsuccessful, we could be subject to costly government enforcement actions and private litigation and our reputation could suffer.
The nature of our business involves the receipt, storage, and transmission of personal and proprietary information about thousands of employees and clients. If we experience a significant data security breach or fail to detect and appropriately respond to a significant data security breach, we could be exposed to government enforcement actions and private litigation. In addition, our employees and clients could lose confidence in our ability to protect their personal and proprietary information, which could cause them to terminate their relationships with us. Any loss of confidence arising from a significant data security breach could hurt our reputation, further damaging our business.
We operate in a complex regulatory environment, and failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations could adversely affect our business.
Corporate human resource operations are subject to a broad range of complex and evolving laws and regulations, including those applicable to payroll practices, benefits administration, employment practices and privacy. Because our clients have employees in many states throughout the United States, we must perform our services in compliance with the legal and regulatory requirements of multiple jurisdictions. Some of these laws and regulations may be difficult to ascertain or interpret and may change from time to time. Violation of such laws and regulations could subject us to fines and penalties, damage our reputation, constitute a breach of our client agreements, impair our ability to obtain and renew required licenses, and decrease our profitability or competitiveness. If any of these effects were to occur, our operating results and financial condition could be adversely affected.
Changes in government regulations may result in restrictions or prohibitions applicable to the provision of employment services or the imposition of additional licensing, regulatory or tax requirements.
Our business is heavily regulated in most jurisdictions in which we operate. We cannot provide assurance that the states in which we conduct or seek to conduct business will not:
|
|
• |
impose additional regulations that prohibit or restrict employment-related businesses like ours; |
|
|
• |
require additional licensing or add restrictions on existing licenses to provide employment-related services; or |
|
|
• |
increase taxes or make changes in the way in which taxes are calculated for providers of employment-related services. |
Any changes in applicable laws and regulations may make it more difficult or expensive for us to do business, inhibit expansion of our business, or result in additional expenses that limit our profitability or decrease our ability to attract and retain clients.
- 18 -
The tax status of our insurance subsidiaries could be challenged resulting in an acceleration of income tax payments.
In conjunction with our workers’ compensation program, we operate two wholly owned insurance subsidiaries, AICE and Ecole. We treat the two subsidiaries as insurance companies for federal income tax purposes with respect to our consolidated federal income tax return. If the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) were to determine that the subsidiaries do not qualify as insurance companies, in which insurance reserves are currently deductible, we could be required to make accelerated income tax payments to the IRS that we otherwise would have deferred until future periods.
We may find it difficult to expand our business into additional states due to varying state regulatory requirements.
Future growth in our operations depends, in part, on our ability to offer our services to prospective clients in new states, which may subject us to different regulatory requirements and standards. In order to operate effectively in a new state, we must obtain all necessary regulatory approvals, adapt our procedures to that state's regulatory requirements and modify our service offerings to adapt to local market conditions. As we expand into additional states, we may not be able to duplicate in other markets the financial performance experienced in our current markets.
We face competition from a number of other companies.
We face competition from various companies that may provide all or some of the services we offer. Our competitors include companies that are engaged in staffing services such as Robert Half International Inc., Kelly Services, Inc., and ManpowerGroup Inc.; companies that are focused on co-employment, such as Insperity, Inc., and TriNet Group, Inc.; and companies that primarily provide payroll processing services, such as Automatic Data Processing, Inc. and Paychex, Inc. We also face competition from information technology outsourcing firms and broad-based outsourcing and consulting firms that perform individual projects.
Several of our existing or potential competitors have substantially greater financial, technical and marketing resources than we do, which may enable them to:
|
|
• |
develop and expand their infrastructure and service offerings more quickly and achieve greater cost efficiencies; |
|
|
• |
invest in new technologies; |
|
|
• |
expand operations into new markets more rapidly; |
|
|
• |
devote greater resources to marketing; |
|
|
• |
compete for acquisitions more effectively and complete acquisitions more easily; and |
|
|
• |
aggressively price products and services and increase benefits in ways that we may not be able to match financially. |
- 19 -
In order to compete effectively in our markets, we must target our potential clients carefully, continue to improve our efficiencies and the scope and quality of our services, and rely on our service quality, innovation, education and program clarity. If our competitive advantages are not compelling or sustainable, then we are unlikely to increase or sustain profits and our stock price could decline.
We are dependent upon certain key personnel and recruitment and retention of key employees may be difficult and expensive.
We believe that the successful operation of our business is dependent upon our retention of the services of key personnel, including our Chief Executive Officer, other executive officers and area managers. We may not be able to retain all of our executives, senior managers and key personnel in light of competition for their services. If we lose the services of one of our executive officers or a significant number of our senior managers, our results of operations likely would be adversely affected.
We do not have an expansive in-house sales staff and therefore rely extensively on referral partners.
We maintain a minimal internal professional sales force, and we rely heavily on referral partners to provide referrals to new business. In connection with these arrangements, we pay a fee to referral partners for new clients. These referral firms and individuals do not have an exclusive relationship with us. If we are unable to maintain these relationships or if they increase their fees or lose confidence in our services, we could face declines in our business and additional costs and uncertainties as we attempt to hire and train an internal sales force.
We depend on attracting and retaining qualified employees; during periods of economic growth, our costs to do so increase and attracting and retaining people becomes more difficult.
Our teams of client-facing professionals are the foundation of our value proposition. Our ability to attract and retain qualified personnel could be impaired by rapid improvement in economic conditions resulting in lower unemployment and increases in compensation. During periods of economic growth, we face increased competition for retaining and recruiting qualified personnel, which in turn leads to greater advertising and recruiting costs and increased salary expenses. If we cannot attract and retain qualified employees, the quality of our services may deteriorate and our reputation and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Our service agreements may be terminated on short notice, leaving us vulnerable to loss of a significant amount of customers in a short period of time, if business or regulatory conditions change or events occur that negatively affect our reputation.
Our client services agreements are generally terminable on 30 days’ notice by either us or our client. As a result, our clients may terminate their agreement with us at any time, making us particularly vulnerable to changing business or regulatory conditions or changes affecting our reputation or the reputation of our industry.
- 20 -
Our industry has at times received negative publicity that, if it were to become more prevalent, could cause our business to decline.
In the staffing and co-employment industries in which we compete, companies periodically have been tarnished by negative publicity or scandals from poor business judgment or even outright fraud. If we or our industry face negative publicity, customers' confidence in the use of temporary personnel or co-employed workers may deteriorate, and they may be unwilling to enter into or continue our staffing or co-employment relationships. If a negative perception were to prevail, it would be more difficult for us to attract and retain customers.
Changes in federal and state unemployment tax laws and regulations could adversely affect our business.
In past years, there has been significant negative publicity relating to the use of staffing or PEO companies to shield employers from poor unemployment history and high unemployment taxes. New legislation enacted at the state or federal level to try to counter this perceived problem could have a material adverse effect on our business by limiting our ability to market our services or making our services less attractive to our customers and potential customers.
Risks Related to Ownership of our Common Stock
Our stock price may be volatile or may decline, resulting in substantial losses for our stockholders.
The market price of our Common Stock has been, and may continue to be, volatile for the foreseeable future. Important factors that may cause our trading price to decline include the factors listed below and other factors that may have a material adverse effect on our business or financial results, including those described above in this “Risk Factors” section:
|
|
• |
actual or anticipated fluctuations in our results of operations, including a significant slowdown in our revenue growth or material increase in our workers’ compensation expense; |
|
|
• |
our failure to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting or otherwise discover additional material errors in our financial reporting; |
|
|
• |
imposition of significant fines or penalties or other adverse action by the SEC or other regulatory authorities against the Company; |
|
|
• |
adverse developments in the legal proceedings described in “Item 3. Legal Proceedings”; |
|
|
• |
our failure to meet financial projections or achieve financial results anticipated by analysts; or |
|
|
• |
changes in our board of directors or management. |
- 21 -
Maryland law and our Charter and bylaws contain provisions that could make the takeover of the Company more difficult.
Certain provisions of Maryland law and our Charter and bylaws could have the effect of delaying or preventing a third party from acquiring the Company, even if a change in control would be beneficial to our stockholders. These provisions of our Charter and bylaws:
|
|
• |
permit the Board of Directors to issue up to 500,000 shares of preferred stock with such rights and preferences, including voting rights, as the Board may establish, without further approval by the Company's stockholders, which could also adversely affect the voting power of holders of our Common Stock; and |
|
|
• |
vest the power to adopt, alter or repeal the Company's bylaws solely in the Board of Directors; the stockholders do not have that power. |
In addition, the Company is subject to the Maryland control share act (the “Control Share Act”). Under the Control Share Act, a person (an “Acquiring Person”) who acquires voting stock in a transaction (a “Control Share Acquisition”) which results in its holding voting power within specified ranges cannot vote the shares it acquires in the Control Share Acquisition unless voting rights are accorded to such control shares by the holders of two-thirds of the outstanding voting shares, excluding the Acquiring Person and the Company's officers and directors who are also employees of the Company.
The Company is also subject to the provisions of Maryland law limiting the ability of certain Maryland corporations to engage in specified business combinations (the “Business Combination Act”). Subject to certain exceptions, the Business Combination Act prohibits a Maryland corporation from engaging in a business combination with a stockholder who, with its affiliates, owns 10% or more of the corporation's voting stock. These provisions will not apply to business combinations that are approved by the Board of Directors before the stockholder became an interested stockholder.
None.
- 22 -
We operate through 57 branch offices. The following table shows the number of locations in each state in which we have offices. We also lease office space in other locations in our market areas which we use to recruit and place employees.
|
|
|
Number of Branch |
|
Offices |
|
Locations |
|
California |
|
21 |
|
Oregon |
|
11 |
|
Utah |
|
5 |
|
Washington |
|
5 |
|
Idaho |
|
3 |
|
Arizona |
|
2 |
|
Colorado |
|
2 |
|
Maryland |
|
2 |
|
North Carolina |
|
2 |
|
Delaware |
|
1 |
|
Nevada |
|
1 |
|
Pennsylvania |
|
1 |
|
Virginia |
|
1 |
We lease office space for our branch offices. At December 31, 2016, our leases had expiration dates ranging from less than one year to seven years, with total minimum payments through 2021 of approximately $13.3 million. Our corporate headquarters occupies approximately 75 percent of the 65,300 square foot building we own in Vancouver, Washington.
On November 6, 2014, plaintiffs in Michael Arciaga, et al. v. Barrett Business Services, Inc., et al., filed an action in the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington against BBSI, Michael L. Elich, BBSI’s Chief Executive Officer, and James D. Miller, BBSI’s then Chief Financial Officer. The action purported to be a class action brought on behalf of all BBSI shareholders alleging violations of the federal securities laws. The claims arose from the decline in the market price for BBSI common stock following announcement of a charge for increased workers’ compensation reserves expense. The lawsuit sought compensatory damages, plus interest, and costs and expenses (including attorney fees and expert fees).
On November 13, 2014, a second purported shareholder class action was filed in the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington, entitled Christopher P. Carnes, et al. v. Barrett Business Services, Inc., et al. The Carnes complaint named the same defendants as the Arciaga case and asserted similar claims for relief.
Similarly, on November 17, 2014, a third purported shareholder class action was filed in the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington, entitled Shiva Stein, et al. v. Barrett Business Services, Inc., et al. The Stein complaint named the same defendants as the Arciaga and Carnes cases and asserted similar claims for relief.
On February 25, 2015, the court ordered consolidation of the three cases, and any new or other cases involving the same subject matter, into a single action for pretrial purposes. The consolidated cases were recaptioned as In re Barrett Business Services Securities
- 23 -
Litigation. The court also appointed the Painters & Allied Trades District Council No. 35 Pension and Annuity Funds as the lead plaintiff.
On March 21, 2016, before the court had ruled on the defendants’ motion to dismiss the plaintiffs’ first amended consolidated complaint, the plaintiffs filed a second amended consolidated complaint, naming the same defendants. The second amended consolidated complaint dropped certain allegations from the first amended complaint and added new allegations relating to disclosures in BBSI’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 9, 2016. The defendants filed a motion to dismiss the second amended consolidated complaint on May 23, 2016.
On October 26, 2016, before the court ruled on the motion to dismiss, the parties entered into a Stipulation and Agreement of Settlement dated as of October 26, 2016 (the “Settlement”), to settle the litigation. The settlement class includes all persons and entities who purchased or otherwise acquired BBSI common stock in the period beginning February 12, 2013, through March 9, 2016, and were damaged thereby, with certain exclusions.
The Settlement is intended to fully, finally and forever compromise, settle, release, resolve, and dismiss with prejudice the purported class action and all claims asserted therein against the named defendants. In the Settlement, the defendants have denied all allegations of wrongdoing and the plaintiffs have not conceded any infirmities in their positions.
The Settlement called for the payment in cash of $12.0 million (the “Settlement Fund”) into escrow by November 29, 2016. Of this amount, approximately $8.7 million was paid by BBSI’s insurance carriers and approximately $3.3 million was paid by BBSI.
The Settlement is subject to approval by the court and to other customary terms and conditions. All potential class members were notified of the Settlement in November 2016, and no requests to opt out of the class were received by the deadline. Final approval of the settlement was received at a court hearing held on February 22, 2017. The fees of counsel for the plaintiffs will be paid out of the Settlement Fund following approval by the court.
BBSI received a subpoena from the San Francisco office of the Division of Enforcement of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) in April 2016 in connection with the SEC’s inquiry into reported errors in our financial statements. The Company previously received a subpoena from the SEC in May 2015 in connection with the SEC’s investigation of the Company’s accounting policies with regard to its workers’ compensation reserves. The Company is cooperating with the SEC investigation. See Item 3 and Note 12 for additional information. Potential civil or criminal proceedings arising out of the SEC investigation could result in the imposition of substantial fines and other penalties on the Company, including those related to failure to keep accurate books and records.
On June 17, 2015, Daniel Salinas (“Salinas”) filed a shareholder derivative lawsuit against BBSI and certain of its officers and directors in the Circuit Court for Baltimore City, Maryland. The complaint alleges breaches of fiduciary duty, unjust enrichment and other violations of law and seeks recovery of various damages, including the costs and expenses incurred in connection with BBSI’s reserve strengthening process, reserve study and consultants, the cost of stock repurchases by BBSI in October 2014, compensation paid to BBSI’s officers, and costs of negotiating BBSI’s credit facility with its principal lender, as well as the proceeds of sales of stock by certain of BBSI’s officers and directors during 2013 and 2014. On September 28, 2015, BBSI and the individual defendants filed motions to dismiss the derivative suit and a motion to stay pending resolution of In re Barrett Business Services
- 24 -
Securities Litigation. On December 4, 2015, Salinas filed an opposition to each motion. On January 27, 2016, the defendants filed a reply to the opposition brief. On February 11, 2016, Judge Michel Pierson heard oral argument on the motions. A decision has not been issued.
Management is unable to estimate the probability, or the potential range of loss arising from the legal actions described above.
BBSI is subject to other legal proceedings and claims, which arise in the ordinary course of our business. In the opinion of management, the amount of ultimate liability with respect to other currently pending or threatened actions is not expected to materially affect BBSI’s consolidated financial position or results of operations.
Not Applicable
- 25 -
|
Item 5. |
MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Our common stock (the "Common Stock") trades on the Global Select Market segment of The Nasdaq Stock Market under the symbol "BBSI." At March 1, 2017, there were 33 stockholders of record and approximately 4,450 beneficial owners of the Common Stock.
The following table presents the high and low sales prices of the Common Stock and cash dividends paid for each quarterly period during the last two fiscal years, as reported by The Nasdaq Stock Market. Any future determination as to the payment of dividends will be made at the discretion of the Board and will depend upon the Company's operating results, financial condition, capital requirements, general business conditions and such other factors as the Board deems relevant. In February 2017, the Board declared a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.25 per share.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Dividends |
|
|
|
|
|
High |
|
|
Low |
|
|
Declared |
|
|||
|
2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Quarter |
|
$ |
44.06 |
|
|
$ |
25.21 |
|
|
$ |
0.22 |
|
|
Second Quarter |
|
|
49.79 |
|
|
|
32.05 |
|
|
|
0.22 |
|
|
Third Quarter |
|
|
45.32 |
|
|
|
32.19 |
|
|
|
0.22 |
|
|
Fourth Quarter |
|
|
53.00 |
|
|
|
34.00 |
|
|
|
0.22 |
|
|
2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Quarter |
|
$ |
42.80 |
|
|
$ |
22.55 |
|
|
$ |
0.22 |
|
|
Second Quarter |
|
|
43.08 |
|
|
|
27.28 |
|
|
|
0.22 |
|
|
Third Quarter |
|
|
49.75 |
|
|
|
41.06 |
|
|
|
0.22 |
|
|
Fourth Quarter |
|
|
66.93 |
|
|
|
43.00 |
|
|
|
0.22 |
|
The Company maintains a Board-approved stock repurchase program which originally authorized up to 3.0 million shares of the Company’s Common Stock to be repurchased from time to time in open market purchases. The repurchase program allowed for the repurchase of approximately 1.1 million shares as of December 31, 2016. No repurchases were made during the quarter ended December 31, 2016.
The following graph shows the cumulative total return at the dates indicated for the period from December 31, 2011 until December 31, 2016, for our Common Stock, The Nasdaq Composite Index, and the S&P 1500 Human Resource & Employment Services Index, a published industry index that is considered more reflective of the Company’s peers. The graph also includes the peer group selected by the Company for 2015 (the “2015 Peer Group”).
- 26 -
The stock performance graph has been prepared assuming that $100 was invested on December 31, 2011 in our Common Stock and the indexes and peer group shown, and that dividends are reinvested. In accordance with the SEC's disclosure rules, the stockholder return for each company in the 2015 Peer Group has been weighted on the basis of market capitalization as of the beginning of each annual period shown. The stock price performance reflected in the graph may not be indicative of future price performance.
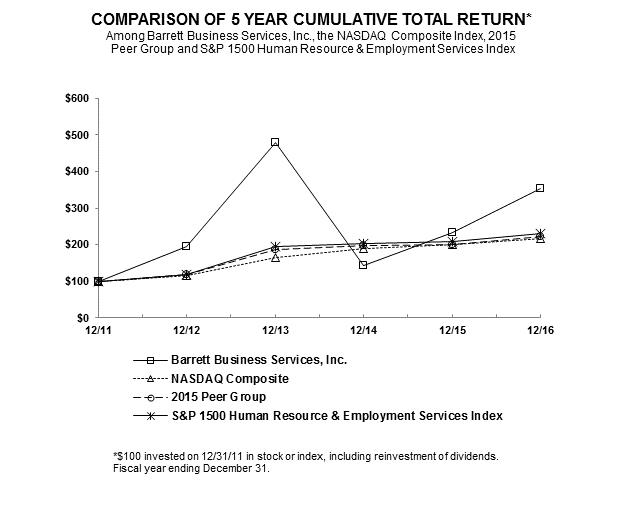
|
|
|
12/11 |
|
|
12/12 |
|
|
12/13 |
|
|
12/14 |
|
|
12/15 |
|
|
12/16 |
|
||||||
|
Barrett Business Services, Inc. |
|
|
100.00 |
|
|
|
194.76 |
|
|
|
478.65 |
|
|
|
144.18 |
|
|
|
234.43 |
|
|
|
353.06 |
|
|
NASDAQ Composite |
|
|
100.00 |
|
|
|
116.41 |
|
|
|
165.47 |
|
|
|
188.69 |
|
|
|
200.32 |
|
|
|
216.54 |
|
|
2015 Peer Group |
|
|
100.00 |
|
|
|
119.06 |
|
|
|
188.00 |
|
|
|
198.49 |
|
|
|
199.99 |
|
|
|
223.39 |
|
|
S&P 1500 Human Resource & Employment Services Index |
|
|
100.00 |
|
|
|
117.53 |
|
|
|
195.39 |
|
|
|
204.13 |
|
|
|
209.03 |
|
|
|
231.76 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Members of 2015 Peer Group |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDI Corp. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Insperity Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kelly Services Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ManpowerGroup Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Robert Half International Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 27 -
The following selected consolidated financial data should be read in conjunction with the Company's consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes incorporated into Item 8 of Part II, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,” and the information contained in Item 7 of Part II, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” Historical results are not necessarily indicative of future results.
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
|
|
2013 |
|
|
|
|
2012 |
|
|||||
|
(In thousands, except per share data) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Unaudited) |
|
|
|
Statement of operations: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Professional employer service fees |
|
$ |
673,924 |
|
|
$ |
572,286 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
470,522 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
393,085 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
277,688 |
|
|
Staffing services |
|
|
166,662 |
|
|
|
168,555 |
|
|
|
|
|
165,833 |
|
|
|
|
|
143,881 |
|
|
|
|
|
126,644 |
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
840,586 |
|
|
|
740,841 |
|
|
|
|
|
636,355 |
|
|
|
|
|
536,966 |
|
|
|
|
|
404,332 |
|
|
Cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct payroll costs |
|
|
126,753 |
|
|
|
127,964 |
|
|
|
|
|
126,399 |
|
|
|
|
|
108,875 |
|
|
|
|
|
95,128 |
|
|
Payroll taxes and benefits |
|
|
357,867 |
|
|
|
312,284 |
|
|
|
|
|
263,100 |
|
|
|
|
|
222,163 |
|
|
|
|
|
167,683 |
|
|
Workers' compensation |
|
|
210,430 |
|
|
|
171,137 |
|
|
|
|
|
213,451 |
|
|
|
|
|
123,427 |
|
|
|
|
|
78,022 |
|
|
Total cost of revenues |
|
|
695,050 |
|
|
|
611,385 |
|
|
|
|
|
602,950 |
|
|
|
|
|
454,465 |
|
|
|
|
|
340,833 |
|
|
Gross margin |
|
|
145,536 |
|
|
|
129,456 |
|
|
|
|
|
33,405 |
|
|
|
|
|
82,501 |
|
|
|
|
|
63,499 |
|
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
113,342 |
|
|
|
90,177 |
|
|
|
|
|
74,065 |
|
|
|
|
|
59,439 |
|
|
|
|
|
45,625 |
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
3,253 |
|
|
|
2,851 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,506 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,037 |
|
|
|
|
|
1,477 |
|
|
Income (loss) from operations |
|
|
28,941 |
|
|
|
36,428 |
|
|
|
|
|
(43,166 |
) |
|
|
|
|
21,025 |
|
|
|
|
|
16,397 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other (expense) income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investment income, net |
|
|
956 |
|
|
|
771 |
|
|
|
|
|
543 |
|
|
|
|
|
539 |
|
|
|
|
|
714 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
|
(807 |
) |
|
|
(1,965 |
) |
|
|
|
|
(173 |
) |
|
|
|
|
(238 |
) |
|
|
|
|
(76 |
) |
|
Loss on litigation |
|
|
(3,544 |
) |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
||||
|
Other, net |
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
(88 |
) |
|
|
|
|
152 |
|
|
|
|
|
(9 |
) |
|
|
|
|
(28 |
) |
|
Other (expense) income |
|
|
(3,355 |
) |
|
|
(1,282 |
) |
|
|
|
|
522 |
|
|
|
|
|
292 |
|
|
|
|
|
610 |
|
|
Income (loss) before income taxes |
|
|
25,586 |
|
|
|
35,146 |
|
|
|
|
|
(42,644 |
) |
|
|
|
|
21,317 |
|
|
|
|
|
17,007 |
|
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
|
|
6,787 |
|
|
|
9,652 |
|
|
|
|
|
(17,098 |
) |
|
|
|
|
5,644 |
|
|
|
|
|
5,424 |
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
18,799 |
|
|
$ |
25,494 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(25,546 |
) |
|
|
|
$ |
15,673 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
11,583 |
|
|
Basic earnings (loss) per common share |
|
$ |
2.60 |
|
|
$ |
3.55 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(3.57 |
) |
|
|
|
$ |
2.21 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
1.50 |
|
|
Weighted average number of basic common shares outstanding |
|
|
7,226 |
|
|
|
7,173 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,160 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,105 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,723 |
|
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per common share |
|
$ |
2.55 |
|
|
$ |
3.47 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(3.57 |
) |
|
|
|
$ |
2.12 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
1.47 |
|
|
Weighted average number of diluted common shares outstanding |
|
|
7,378 |
|
|
|
7,353 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,160 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,397 |
|
|
|
|
|
7,863 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash dividends per common share |
|
$ |
0.88 |
|
|
$ |
0.88 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
0.76 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
0.57 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
0.46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selected balance sheet data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
50,768 |
|
|
$ |
25,218 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
11,544 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
93,557 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
45,747 |
|
|
Investments |
|
|
6,317 |
|
|
|
6,082 |
|
|
|
|
|
50,887 |
|
|
|
|
|
25,696 |
|
|
|
|
|
26,647 |
|
|
Current assets |
|
|
260,625 |
|
|
|
227,009 |
|
|
|
|
|
182,802 |
|
|
|
|
|
214,286 |
|
|
|
|
|
142,417 |
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
|
275,164 |
|
|
|
237,393 |
|
|
|
|
|
225,302 |
|
|
|
|
|
153,988 |
|
|
|
|
|
115,711 |
|
|
Working capital (deficit) surplus |
|
|
(14,539 |
) |
|
|
(10,384 |
) |
|
|
|
|
(42,500 |
) |
|
|
|
|
60,298 |
|
|
|
|
|
26,706 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
|
597,760 |
|
|
|
496,777 |
|
|
|
|
|
452,401 |
|
|
|
|
|
316,723 |
|
|
|
|
|
231,860 |
|
|
Long-term workers' compensation liabilities |
|
|
231,198 |
|
|
|
190,094 |
|
|
|
|
|
164,214 |
|
|
|
|
|
79,849 |
|
|
|
|
|
49,737 |
|
|
Long-term debt, net of current portion |
|
|
4,392 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
19,833 |
|
|
|
|
|
5,053 |
|
|
|
|
|
5,273 |
|
|
|
Stockholders' equity |
|
|
69,693 |
|
|
|
54,551 |
|
|
|
|
|
32,820 |
|
|
|
|
|
65,177 |
|
|
|
|
|
48,740 |
|
The net loss in 2014 is primarily due to expense associated with an increase in the Company’s reserve for workers’ compensation claims liabilities of approximately $104.2 million.
- 28 -
See “Note 5. Workers’ Compensation Claims” to the consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this report.
- 29 -
Overview
The Company is a leading provider of business management solutions for small and mid-sized companies. The Company has developed a management platform that integrates a knowledge-based approach from the management consulting industry with tools from the human resource outsourcing industry. This platform, through the effective leveraging of human capital, helps our business owner clients run their businesses more effectively. We believe this platform, delivered through a decentralized organizational structure, differentiates BBSI from our competitors.
We report revenues in our financial results in two categories of services: professional employer services (“PEO”) and staffing.
With our PEO clients, we enter into a co-employment arrangement in which we become the administrative employer while the client maintains physical care, custody and control of their workforce. Our PEO services are billed as a percentage of client payroll, with the gross amount invoiced including direct payroll costs, employer payroll-related taxes, workers’ compensation coverage (if provided) and a service fee. PEO customers are invoiced following the end of each payroll processing cycle and are generally due on the invoice date. Revenues for PEO services exclude direct payroll billings because we are not the primary obligor for those payments.
We generate staffing services revenues primarily from short-term staffing, contract staffing, on-site management and direct placement services. For staffing services other than direct placement, invoiced amounts include direct payroll, employer payroll-related taxes, workers’ compensation coverage and a service fee. Staffing customers are invoiced weekly and typically have payment terms of 30 days. Direct placement services are billed at agreed fees at the time of a successful placement.
Our business is concentrated in California, and we expect to continue to derive a majority of our revenues from this market in the future. Revenues generated in our California offices accounted for 78% of our total net revenues in 2016, 78% in 2015 and 77% in 2014. Consequently, any weakness in economic conditions or changes in the regulatory or insurance environment in California could have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
Our cost of revenues for PEO services includes employer payroll-related taxes and workers' compensation costs. Our cost of revenues for staffing services includes direct payroll costs, employer payroll-related taxes, employee benefits, and workers’ compensation costs. Direct payroll costs represent the gross payroll earned by staffing services employees based on salary or hourly wages. Payroll taxes and employee benefits consist of the employer's portion of Social Security and Medicare taxes, federal and state unemployment taxes and staffing services employee reimbursements for materials, supplies and other expenses, which are paid by our customer. Workers' compensation costs consist primarily of the costs associated with our workers' compensation program, including claims reserves, claims administration fees, legal fees, medical cost containment (“MCC”) expense, state administrative agency fees, third-party broker commissions, risk manager payroll, premiums for excess insurance and the fronted insurance program, and costs associated with operating our two wholly owned, fully-licensed insurance companies, AICE and Ecole.
- 30 -
The largest portion of workers' compensation expense is the cost of workplace injury claims. When an injury occurs and is reported to us, our respective independent third-party administrator for workers’ compensation claims (“TPA”) or our internal claims management personnel analyzes the details of the injury and develops a case reserve, which becomes the estimate of the cost of the claim based on similar injuries and their professional judgment. We then record an expense and a corresponding liability based on our estimate of the ultimate claim cost. As cash payments are made by our TPA against specific case reserves, the accrued liability is reduced by the corresponding payment amount. The TPA and our in-house claims administrators also review existing injury claims on an on-going basis and adjust the case reserves as additional information for each claim becomes available. Our reserve includes a provision both for future anticipated increases in costs ("adverse loss development") of open claims and for claims incurred but not reported related to prior and current periods (together, “IBNR”). This provision for IBNR represents our independent actuary’s best estimate of future payments the Company will make related to workers’ compensation claims in excess of initial case reserves. We believe our operational policies and internal claims reporting system help to limit the amount of incurred but unreported claims.
Selling, general and administrative expenses represent both branch office and corporate-level operating expenses. Branch operating expenses consist primarily of branch office staff payroll and personnel related costs, advertising, rent, office supplies, professional and legal fees and branch incentive compensation. Corporate-level operating expenses consist primarily of executive and office staff payroll and personnel related costs, professional and legal fees, travel, occupancy costs, information systems costs, and executive and corporate staff incentive compensation.
Depreciation and amortization represent depreciation of property and equipment, leasehold improvements and capitalized software costs. Property, equipment and software are depreciated using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, which range from 3 to 39 years. Leasehold improvements are amortized using the straight-line method over the shorter of the lease term or estimated useful life.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
We have identified the following policies as critical to our business and the understanding of our results of operations. For a detailed discussion of the application of these and other accounting policies, see “Note 1. Summary of Operations and Significant Accounting Policies” to the consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this report. The preparation of this Annual Report on Form 10-K requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Workers' Compensation Reserves. The estimated liability for unsettled workers' compensation claims represents our best estimate, utilizing actuarial expertise and projection techniques, at a given reporting date. Our estimate is based on an evaluation of information provided by our internal claims adjusters and TPA, coupled with management's use of an independent actuary to provide an actuarial estimate of IBNR costs. These elements serve as the basis for our overall estimate of workers' compensation claims liabilities. These estimates
- 31 -
are reviewed at least quarterly and adjustments to estimated liabilities are reflected in current operating results as they become known.
IBNR is based on an estimate of future claim payments beyond those considered in the specific case reserve estimates and claims arising from injuries that occurred during a particular time period on or prior to the balance sheet date. Therefore, IBNR is the compilation of the estimated ultimate losses for each accident year less amounts that have been paid and specific case reserves. IBNR reserves, unlike specific case reserves, do not apply to a specific claim but rather apply to the entire body of claims arising from a specific time period. IBNR primarily covers costs relating to:
|
|
• |
Future claim payments in excess of case reserves on recorded open claims; |
|
|
• |
Additional claim payments on closed claims; and |
|
|
• |
Claims that have occurred but have not yet been reported to us. |
The process of estimating unpaid claims and claims adjustment expense involves a high degree of judgment and is affected by both internal and external events, including changes in claims handling practices, modifications in reserve estimation procedures, changes in individuals involved in the reserve estimation process, inflation, trends in the litigation and settlement of pending claims, and legislative changes.
Our estimates are based on informed judgment, derived from individual experiences and expertise applied to multiple sets of data and analyses. We consider significant facts and circumstances known both at the time that loss reserves are initially established and as new facts and circumstances become known. Due to the inherent uncertainty underlying loss reserve estimates, the expenses incurred through final resolution of our liability for our workers’ compensation claims will likely vary from the related loss reserves at the reporting date. Therefore, as specific claims are paid out in the future, actual paid losses may be materially different from our current loss reserves.
A basic premise in most actuarial analyses is that historical data and past patterns demonstrated in the incurred and paid historical data form a reasonable basis upon which to project future outcomes, absent a material change. Significant structural changes to the available data can materially impact the reserve estimation process. To the extent a material change affecting the ultimate claim liability becomes known, such change is quantified to the extent possible through an analysis of internal company data and, if available and when appropriate, external data. Actuaries exercise a considerable degree of judgment in the evaluation of these factors and the need for such actuarial judgment is more pronounced when faced with material uncertainties.
We believe that the amounts recorded for our estimated liabilities for workers’ compensation claims, which are based on informed judgement, analysis of data, actuarial estimates, and analysis of other trends associated with the Company’s historical universe of claims data, are reasonable. Nevertheless, adjustments to such estimates will be required in future periods if the development of claim costs varies materially from our estimates and such future adjustments may be material to our results of operations.
Safety Incentives Liability. Our accrued safety incentives represent cash incentives paid to certain PEO clients under our client services agreement for maintaining safe-work practices and minimizing workplace injuries. The incentive is based on a percentage of annual payroll and is
- 32 -
paid annually to customers who meet predetermined workers’ compensation claims cost objectives. Safety incentive payments are made only after closure of all workers’ compensation claims incurred during the customer’s contract period. The safety incentive liability is estimated and accrued each month based upon contract year-to-date payroll and the then current amount of the customer’s estimated workers’ compensation claims reserves as established by us and our TPA. Safety incentive costs are netted against PEO service revenue in our consolidated statements of operations. Because the safety incentive liability is dependent on estimated claims costs, the amount accrued will vary based on the factors described above with regard to estimating our workers’ compensation reserves.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. The Company had an allowance for doubtful accounts of $78,000 and $268,000 at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. We make estimates of the collectability of our accounts receivable for services provided to our customers. Management analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit-worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customers' payment trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts. If the financial condition of our customers deteriorates, resulting in an impairment of their ability to make payments, additional allowances may be required.
Goodwill. We assess the recoverability of goodwill annually for potential impairment for the Company’s one reporting unit. Management uses the traditional two step approach to determine if the fair value of the reporting unit does not exceed its carrying value, thus resulting in impairment. Management defines the fair value of the reporting unit as the market value of common shares outstanding as of the reporting period end date. Management defines the reporting unit’s carrying value as the value of its net assets. Management’s current assessment of the carrying value of goodwill indicates there was no impairment as of December 31, 2016.
Investments. We classify our investments as trading or available-for-sale. The Company had no trading securities at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015. The Company classifies money market funds, municipal bonds, and corporate bonds as available for sale. They are reported at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of taxes, shown as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in stockholders' equity. Management considers available evidence in evaluating potential impairment of investments, including the duration and extent to which fair value is less than cost. Realized gains and losses on sales of investments are included in other income (expense) as other, net in our consolidated statements of operations. In the event a loss is determined to be other-than-temporary, the loss will be recognized in the consolidated statements of operations.
Restricted Cash and Investments. At December 31, 2016, restricted cash and investments consisted of money market funds, certificates of deposit, U.S. Treasuries, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds with maturities generally from 180 days to two years. At December 31, 2016, the approximate fair value of restricted cash and investments equaled their approximate amortized cost. Restricted investments have been categorized as available-for-sale. They are reported at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of taxes, shown as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in stockholders’ equity. Management considers available evidence in evaluating potential impairment of investments, including the duration and extent to which fair value is less than cost. Realized gains and losses on sales of restricted investments are included in other income (expense) as other, net in our consolidated statements of operations. In the event a loss is determined to be other-than-temporary, the loss will be recognized in the consolidated statements of operations.
- 33 -
Income Taxes. Our income taxes are accounted for using an asset and liability approach. This requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities at the applicable tax rates. The determination of our provision for income taxes requires significant judgment, the use of estimates, and the interpretation and application of complex tax laws. Significant judgment is required in assessing the timing and amounts of deductible and taxable items and the probability of sustaining uncertain tax positions. The impact of uncertain tax positions would be recorded in our financial statements only after determining a more-likely-than-not probability that the uncertain tax positions would withstand challenge, if any, from taxing authorities. At December 31, 2016, we had deferred income tax assets of $25.2 million and deferred income tax liabilities of $15.9 million for net deferred income tax assets of $9.3 million.
We assess our ability to realize deferred income tax assets at each reporting period, as significant changes in circumstances may require adjustments. The amount of the deferred income tax assets actually realized could vary if there are differences in the timing or amount of future reversals of existing deferred income tax assets or changes in the actual amounts of future taxable income as compared to operating forecasts. If our operating forecast is determined to no longer be reliable due to uncertain market conditions, our long-term forecast may require reassessment. As a result, in the future a valuation allowance may be required to be established for all or a portion of our deferred income tax assets. Such a valuation allowance could have a significant effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
For a discussion of recent accounting pronouncements and their potential effect on the Company's results of operations and financial condition, see “Note 1. Summary of Operations and Significant Accounting Policies” to the consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this report.
Forward-Looking Information
Statements in this Item or in Items 1, 1A, 3 and 9A of this report include forward-looking statements which are not historical in nature. These forward-looking statements include, among others, discussion of economic conditions in our market areas and their effect on revenue levels, the effect of changes in our mix of services on gross margin, the need to continue to retain customers following price increases, the adequacy of our workers' compensation reserves, the effect of changes in estimates of our future claims liabilities on our workers’ compensation reserves, including the effect of changes in our reserving practices and claims management process on our actuarial estimates, our ability to generate sufficient taxable income in the future to utilize our deferred tax assets, the effect of our formation and operation of two wholly owned fully licensed insurance subsidiaries, the effects of becoming self-insured for certain business risks, the risks of operation and cost of our fronted insurance program with Chubb, the effects of material weaknesses in our internal control environment, our ability to pass on increased costs relating to the mandate to provide health insurance coverage to our clients, the cost of providing healthcare coverage to staffing employees, the financial viability of our excess insurance carriers, the effectiveness of our management information systems, our relationship with our primary bank lender and the availability of financing and working capital to meet our funding requirements, compliance with the continued listing requirements of The Nasdaq Stock Market (“NASDAQ”), current and future shareholder litigation, ongoing investigations by the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) and the United States Department of Justice (“the DOJ”), the effect of changes in the interest rate environment on the value of our investment securities and long-term debt, the adequacy of our allowance for
- 34 -
doubtful accounts, and the potential for and effect of acquisitions, are forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995.
All of our forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause the actual results, performance or achievements of the Company or industry to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Such factors with respect to the Company include our ability to retain current clients and attract new clients, difficulties associated with integrating clients into our operations, economic trends in our service areas, the potential for material deviations from expected future workers’ compensation claims experience, the effect of changes in the workers’ compensation regulatory environment in one or more of our primary markets, collectability of accounts receivable, the carrying values of deferred income tax assets and goodwill (which may be affected by our future operating results), the cost of defending against or settling shareholder litigation, the expenses associated with cooperating in the SEC and DOJ investigations and the potential imposition of fines, penalties and other remedies, the costs of remediating material weaknesses in our internal control environment, the impact of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and escalating medical costs on our business, the effect of conditions in the global capital markets on our investment portfolio, and the availability of capital, borrowing capacity on our revolving credit facility, or letters of credit necessary to meet state-mandated surety deposit requirements for maintaining our status as a qualified self-insured employer for workers' compensation coverage or our fronted insurance program. Additional risk factors affecting our business are discussed in Item 1A of Part I of this report. We disclaim any obligation to update any such factors or to publicly announce any revisions to any of the forward-looking statements contained herein to reflect future events or developments.
- 35 -
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth the percentages of total revenues represented by selected items in the Company's consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, included in Item 15 of this report. References to the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements appearing below are to the notes to the Company's consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this report.
|
|
|
Percentage of Total Net Revenues |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
($ in thousands) |
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Professional employer service fees |
$ |
|
673,924 |
|
|
|
80.2 |
|
% |
$ |
|
572,286 |
|
|
|
77.2 |
|
% |
$ |
|
470,522 |
|
|
|
73.9 |
|
% |
|
Staffing services |
|
|
166,662 |
|
|
|
19.8 |
|
|
|
|
168,555 |
|
|
|
22.8 |
|
|
|
|
165,833 |
|
|
|
26.1 |
|
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
840,586 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
|
740,841 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
|
636,355 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
|
|
|
Cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct payroll costs |
|
|
126,753 |
|
|
|
15.1 |
|
|
|
|
127,964 |
|
|
|
17.3 |
|
|
|
|
126,399 |
|
|
|
19.9 |
|
|
|
Payroll taxes and benefits |
|
|
357,867 |
|
|
|
42.6 |
|
|
|
|
312,284 |
|
|
|
42.1 |
|
|
|
|
263,100 |
|
|
|
41.4 |
|
|
|
Workers' compensation |
|
|
210,430 |
|
|
|
25.0 |
|
|
|
|
171,137 |
|
|
|
23.1 |
|
|
|
|
213,451 |
|
|
|
33.5 |
|
|
|
Total cost of revenues |
|
|
695,050 |
|
|
|
82.7 |
|
|
|
|
611,385 |
|
|
|
82.5 |
|
|
|
|
602,950 |
|
|
|
94.8 |
|
|
|
Gross margin |
|
|
145,536 |
|
|
|
17.3 |
|
|
|
|
129,456 |
|
|
|
17.5 |
|
|
|
|
33,405 |
|
|
|
5.2 |
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
113,342 |
|
|
|
13.5 |
|
|
|
|
90,177 |
|
|
|
12.2 |
|
|
|
|
74,065 |
|
|
|
11.6 |
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
3,253 |
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
2,851 |
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
2,506 |
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
Income (loss) from operations |
|
|
28,941 |
|
|
|
3.4 |
|
|
|
|
36,428 |
|
|
|
4.9 |
|
|
|
|
(43,166 |
) |
|
|
(6.8 |
) |
|
|
Other (expense) income |
|
|
(3,355 |
) |
|
|
(0.4 |
) |
|
|
|
(1,282 |
) |
|
|
(0.2 |
) |
|
|
|
522 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
Income (loss) before income taxes |
|
|
25,586 |
|
|
|
3.0 |
|
|
|
|
35,146 |
|
|
|
4.7 |
|
|
|
|
(42,644 |
) |
|
|
(6.7 |
) |
|
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
|
|
6,787 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
9,652 |
|
|
|
1.3 |
|
|
|
|
(17,098 |
) |
|
|
(2.6 |
) |
|
|
Net income (loss) |
$ |
|
18,799 |
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
% |
$ |
|
25,494 |
|
|
|
3.4 |
|
% |
$ |
|
(25,546 |
) |
|
|
(4.1 |
) |
% |
We report PEO revenues on a net basis because we are not the primary obligor for certain of the services provided to our clients on behalf of their employees pursuant to our client services agreements. We present for comparison purposes the gross revenues and cost of revenues information for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 in the table below. Although not in accordance with GAAP, management believes this information is informative as to the level of our business activity and illustrative of how we manage our operations, including the preparation of our internal operating forecasts, because it presents our professional employer services on a basis comparable to our staffing services.
The presentation of revenues on a net basis and the relative contributions of staffing and professional employer services revenues can create volatility in our gross margin percentage. The general impact of fluctuations in our revenue mix is described below.
|
|
• |
A relative increase in professional employer services revenue will result in a higher gross margin percentage. Improvement in gross margin percentage occurs because incremental client services revenue dollars are reported as revenue net of all related direct payroll and safety incentive costs. |
- 36 -
|
|
• |
A relative increase in staffing revenues will typically result in a lower gross margin percentage. Staffing revenues are presented at gross with the related direct costs reported in cost of revenues. While staffing relationships typically have higher margins than professional employer service relationships, an increase in staffing revenues and related costs increases the impact of the net professional employer services revenue on gross margin percentage. |
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
(in thousands) |
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
Gross revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Professional employer services |
|
$ |
4,526,225 |
|
|
$ |
3,847,595 |
|
|
Staffing services |
|
|
166,662 |
|
|
|
168,555 |
|
|
Total gross revenues |
|
|
4,692,887 |
|
|
|
4,016,150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct payroll costs |
|
|
3,951,021 |
|
|
|
3,375,976 |
|
|
Payroll taxes and benefits |
|
|
357,867 |
|
|
|
312,284 |
|
|
Workers' compensation |
|
|
238,463 |
|
|
|
198,434 |
|
|
Total gross cost of revenues |
|
|
4,547,351 |
|
|
|
3,886,694 |
|
|
Gross margin |
|
$ |
145,536 |
|
|
$ |
129,456 |
|
A reconciliation of net revenue to non-GAAP gross revenues is as follows for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 (in thousands):
|
|
|
Net Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross Revenue |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Reporting Method (GAAP) |
|
|
Non-GAAP Adjustments |
|
|
Reporting Method (Non-GAAP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||||||||
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Professional employer services |
|
$ |
673,924 |
|
|
$ |
572,286 |
|
|
$ |
470,522 |
|
|
$ |
3,852,301 |
|
|
$ |
3,275,309 |
|
|
$ |
2,720,707 |
|
|
$ |
4,526,225 |
|
|
$ |
3,847,595 |
|
|
$ |
3,191,229 |
|
|
Staffing services |
|
|
166,662 |
|
|
|
168,555 |
|
|
|
165,833 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
166,662 |
|
|
|
168,555 |
|
|
|
165,833 |
|
|
Total revenues |
|
$ |
840,586 |
|
|
$ |
740,841 |
|
|
$ |
636,355 |
|
|
$ |
3,852,301 |
|
|
$ |
3,275,309 |
|
|
$ |
2,720,707 |
|
|
$ |
4,692,887 |
|
|
$ |
4,016,150 |
|
|
$ |
3,357,062 |
|
|
Cost of revenues: |
|
$ |
695,050 |
|
|
$ |
611,385 |
|
|
$ |
602,950 |
|
|
$ |
3,852,301 |
|
|
$ |
3,275,309 |
|
|
$ |
2,720,707 |
|
|
$ |
4,547,351 |
|
|
$ |
3,886,694 |
|
|
$ |
3,323,657 |
|
The non-GAAP adjustments comprise direct payroll costs and safety incentives attributable to our professional employer services client companies.
Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
Net income for 2016 amounted to $18.8 million compared to net income of $25.5 million for 2015. Net income in 2016 was primarily driven by a 13.5% increase in revenues and a 12.4% increase in gross margin. The increase in gross margin in 2016 is primarily due to the large increase in professional employer service fee revenue from 2015 to 2016. Diluted income per share for 2016 was $2.55 compared to diluted income per share of $3.47 for 2015.
Revenues for 2016 totaled $840.6 million, an increase of $99.7 million or 13.5% over 2015, which reflects an increase in the Company’s professional employer service fee revenue of $101.6 million or 17.8%. Staffing services revenue decreased $1.9 million or 1.1%.
- 37 -
Our growth in professional employer service revenues was attributable to both new and existing customers. Due to continued strength in our referral channels, business from new customers during 2016 nearly doubled business lost from former customers. Professional employer service revenue from continuing customers grew 6.8% on a year-over-year basis, primarily resulting from increases in employee headcount and hours worked. The decrease in staffing services revenue was due primarily to a decrease in revenue from continuing customers, partially offset by an increase in net staffing revenue from new customers over lost customers.
During 2016, the Company served approximately 4,972 PEO clients, compared to approximately 4,195 PEO clients during 2015. During 2016, the Company served approximately 1,531 staffing services customers, compared to 1,770 during 2015.
Gross margin for 2016 totaled $145.5 million or 17.3% of revenue compared to $129.5 million or 17.5% of revenue for 2015. The decrease in gross margin percentage was primarily due to increases in workers’ compensation expense and payroll taxes and benefits, partially offset by a decrease in direct payroll costs.
Direct payroll costs for 2016 totaled $126.8 million or 15.1% of revenue compared to $128.0 million or 17.3% of revenue for 2015. The decrease in direct payroll costs percentage was primarily due to the increase in professional employer services and the decrease of staffing services within the mix of our customer base compared to 2015.
Payroll taxes and benefits for 2016 totaled $357.9 million or 42.6% of revenue compared to $312.3 million or 42.1% of revenue for 2015. The increase in payroll taxes and benefits percentage was primarily due to the effect of growth in professional employer services, where payroll taxes and benefits are presented at gross cost.
Workers’ compensation expense for 2016 totaled $210.4 million or 25.0% of revenue compared to $171.1 million or 23.1% of revenue for 2015. The increase in workers’ compensation expense as a percentage of revenue was primarily due to a decrease in our workers’ compensation reserves in 2015 of $13.7 million related to actuarial adjustments in that year.
Selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”) expenses for 2016 totaled $113.3 million, or 13.5% of revenue compared to $90.2 million or 12.2% of revenue for 2015. The increase was primarily attributable to an increase in management payroll expense from $41.8 million in 2015 to $49.1 million in 2016. A portion of the increase was due to $11.0 million in total legal and accounting expenses, of which $8.5 million pertained to non-recurring legal and accounting costs associated with financial restatements, outside investigations, and legal proceedings related to securities law issues.
Other expense for 2016 totaled $3.4 million compared to $1.3 million for 2015. The change was attributable to a $3.3 million litigation settlement recognized in the third quarter of 2016, partially offset by a decline in interest expense and an increase in investment income.
Our effective income tax rate for 2016 was 26.5% compared to 27.5% for 2015. Our income tax rate typically differs from the federal statutory tax rate of 35% primarily due to federal and state tax credits. See “Note 9. Income Taxes” to the consolidated financial statements incorporated into Item 8 of Part II of this report for additional information regarding income taxes.
- 38 -
Years Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
Net income for 2015 was $25.5 million compared to net loss of $25.5 million for 2014. Net income in 2015 was primarily driven by a 16.4% increase in revenues and a 12.3% increase in gross margin percentage. The increase in gross margin in 2015 is primarily due to the large decrease in worker’s compensation expense from 2014 to 2015. Diluted income per share for 2015 was $3.47 compared to a diluted loss per share of $3.57 for 2014.
Revenues for 2015 of $740.9 million reflect an increase in the Company’s professional employer service fee revenue of $101.8 million or 21.6%, coupled with an increase in staffing services revenue of $2.7 million or 1.6%.
Our growth in professional employer service revenues was attributable to both new and existing customers. Due to continued strength in our referral channels, business from new customers during 2015 nearly doubled business lost from former customers during that year. Professional employer service revenue from continuing customers grew 10.2% on a year-over-year basis, primarily resulting from increases in employee headcount and hours worked. The increase in staffing services revenue was due primarily to growth in new customers as well as the addition of new business, partially offset by lost business from former customers.
During 2015 the Company served approximately 4,195 PEO clients, compared to approximately 3,665 PEO clients during 2014. During 2015 the Company served approximately 1,770 staffing services customers, compared to 1,825 during 2014.
Gross margin for 2015 totaled $129.5 million or 17.5% of revenue compared to $33.4 million or 5.2% of revenue for 2014. The 12.3% increase in gross margin percentage was primarily due to decreases in workers’ compensation expense and direct payroll costs, partially offset by an increase in payroll taxes and benefits.
Workers' compensation expense decreased from $213.5 million or 33.5% of revenue in 2014 to $171.1 million or 23.1% of revenue in 2015. The decrease was primarily driven by the Company’s large worker’s compensation expense change of $84.7 million taken in the second quarter of 2014.
In 2014, after extensive analysis, management concluded that a significant increase in workers’ compensation liability was needed, primarily to reflect the potential adverse development of prior period claims. Management’s primary considerations in determining to record a large increase in the Company’s estimate of workers’ compensation liability in 2014 included the large increase in the Company’s business in recent years, the potential for large future adverse development of open claims, and the increasing complexity and uncertainty surrounding healthcare costs. In 2015, as the actuarial data began to stabilize, we did not see the significant adverse development on prior years’ claims compared to 2014.
The Company recorded $225.7 million and $225.3 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, as an estimated future liability for workers’ compensation claims liabilities. The estimated liabilities for workers’ compensation claims represent management’s best estimate based upon an actuarial valuation provided by a third party actuary at December 31, 2015 and 2014.
Direct payroll costs as a percentage of revenues decreased to 17.3% for 2015 from 19.9% for 2014, primarily due to the increase in our mix of professional employer services in the Company’s customer base compared to 2014.
- 39 -
Payroll taxes and benefits as a percentage of revenues for 2015 was 42.2% compared to 41.4% for 2014. The percentage rate increase was primarily due to the effect of growth in professional employer services. The effect of the growth in professional employer services on payroll taxes and benefits was partially offset by a decline in the overall state unemployment tax rates where the Company does business.
SG&A expenses for 2015 were $90.2 million, an increase of $16.1 million or 21.8% over 2014. The increase was primarily attributable to an increase in management payroll, information technology (“IT”) expenses, and other variable expense components within SG&A to support our business growth. The increased IT expenses relate to projects designed to enhance access and delivery of information to the field as well as to improve efficiencies over time. SG&A expenses as a percentage of revenues increased from 11.6% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2015.
Other expense for 2015 was $1.3 million compared to other income of $522,000 for 2014 due to an increase in interest expense of $1.8 million resulting from the Company’s $40.0 million term loan entered into on December 29, 2014.
Our effective income tax rate for 2015 was 27.5%, as compared to (40.1)% for 2014 due to our loss from operations. Our income tax rate typically differs from the federal statutory tax rate of 35% primarily due to federal and state tax credits.
Fluctuations in Quarterly Operating Results
We have historically experienced significant fluctuations in our quarterly operating results, including losses in the first quarter of each year, and expect such fluctuations to continue in the future. Our operating results may fluctuate due to a number of factors such as seasonality, wage limits on statutory payroll taxes, claims experience for workers’ compensation, demand for our services and competition. Payroll taxes, as a component of cost of revenues, generally decline throughout a calendar year as the applicable statutory wage bases for federal and state unemployment taxes and Social Security taxes are exceeded on a per employee basis. Our revenue levels may be higher in the third quarter due to the effect of increased business activity of our customers’ businesses in the agriculture, food processing and forest products-related industries. In addition, revenues in the fourth quarter may be reduced by many customers’ practice of operating on holiday-shortened schedules. Workers’ compensation expense varies with both the frequency and severity of workplace injury claims reported during a quarter and the estimated future costs of such claims. Adverse loss development of prior period claims during a subsequent quarter may also contribute to the volatility in the Company’s estimated workers’ compensation expense.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company's cash position of $50.8 million at December 31, 2016 increased $25.6 million compared to December 31, 2015. The increase in cash at December 31, 2016 as compared to December 31, 2015 was primarily due to a decrease in purchases of restricted cash and investments of $150.3 million, an increase in accrued payroll, payroll taxes and related benefits of $26.3 million, an increase of workers’ compensation claims liabilities of $20.8 million, and a decrease in payments on long-term debt of $10.0 million. Increases in the Company’s cash position were partially offset by decreased proceeds from sales and maturities of restricted cash and investments of $84.8 million, decreased proceeds from sales and maturities of unrestricted investments of $48.2 million, and increased cash outflows related to net trade accounts receivable of $48.1 million.
Net cash provided by operating activities in 2016 amounted to $80.3 million, compared to $100.6 million for 2015. In 2016, cash flow was primarily provided by net income of $18.8
- 40 -
million, workers’ compensation claims liabilities of $51.2 million and accrued payroll, payroll taxes and related benefits of $31.8 million, partially offset by cash outflows related to net trade accounts receivable of $36.0 million.
Net cash used in investing activities totaled $33.1 million in 2016, compared to $55.6 million in 2015. In 2016, cash used in investing activities consisted primarily of purchases of restricted cash and investments of $185.8 million, partially offset by proceeds from sales and maturities of restricted cash and investments of $153.9 million.
Net cash used in financing activities in 2016 was $21.7 million compared to $31.4 million for 2015. In 2016, cash was primarily used for payments on long-term debt of $15.2 million and dividends of $6.4 million.
The states of California, Maryland, Oregon, Washington, Colorado and Delaware required us to maintain specified investment balances or other financial instruments totaling $135.0 million and $156.8 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, to cover potential workers’ compensation claims losses related to the Company’s current and former status as a self-insured employer. In addition to restricted cash and investments held to satisfy these requirements, at December 31, 2016, we have provided surety bonds and standby letters of credit totaling $128.8 million, including a California requirement of $123.3 million. In conjunction with these letters of credit, the Company posted $5.3 million in restricted certificates of deposit as collateral.
Due to the Company’s stronger financial position and market competition, the surety insurers decreased their letter of credit requirement to $5.0 million at December 31, 2016 from $88.3 million at December 31, 2015. The collateral associated with the letters of credit decreased to $5.3 million at December 31, 2016 from $92.4 million at December 31, 2015.
Management expects the surety bonds, letters of credit and related collateral to continue to decrease over time as a result of paying down the self-insured liability in California. The Company’s self-insured status in California ended on December 31, 2014.
Ecole, our wholly owned insurance company, provides workers’ compensation coverage to the Company’s employees working in Arizona, Utah and Nevada. The surplus of Ecole was $12.1 million and $9.5 million at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively, and is included in long-term restricted cash and investments in our consolidated balance sheets.
As part of its fronted workers’ compensation insurance program with Chubb, the Company makes monthly payments into a trust account (“the Chubb trust account”) to be used for the payment of future claims. The balance in the Chubb trust account was $277.1 million and $166.6 million at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively. The Chubb trust account balances are included as a component of the current and long-term restricted cash and investments in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets.
The Company maintains a credit agreement (the “Agreement”) with its principal bank, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association (the “Bank”). The Agreement provided for a $40.0 million term loan maturing December 31, 2016. The term loan has been completely paid off at December 31, 2016, compared to an outstanding balance of $15.0 million at December 31, 2015.
The Agreement was amended in December 2016 to increase our revolving credit line to $25.0 million, with a $6.0 million sublimit for standby letters of credit. Of the $6.0 million sublimit
- 41 -
for standby letters of credit, $5.3 million was used at December 31, 2016. Advances under the revolving credit facility bear interest, as selected by the Company, of either (a) a daily floating rate of one month LIBOR plus 1.75% or (b) a fixed rate of LIBOR plus 1.75%. The Agreement also provides for an unused commitment fee of 0.35% per year through December 31, 2016 and 0.375% per year thereafter on the average daily unused amount of the revolving credit facility, and a fee of 1.75% of the face amount of each letter of credit reserved under the line of credit and 0.95% on standalone, fully secured letters of credit. The Company had no outstanding borrowings on its revolving credit line at December 31, 2016 and 2015. The line of credit expires on July 1, 2018.
The Agreement includes $5.0 million in standalone, cash-secured letters of credit at December 31, 2016 to satisfy collateral requirements associated with the Company’s former status as a self-insured employer in California. In conjunction with these letters of credit, the Company posted with the Bank as collateral $5.3 million in restricted certificates of deposit.
The credit facility is collateralized by the Company’s accounts receivable and other rights to receive payment, general intangibles, inventory and equipment.
The Agreement requires the satisfaction of certain financial covenants as follows:
|
|
• |
EBITDA [net profit before taxes plus interest expense (net of capitalized interest expense), depreciation expense, and amortization expense] on a rolling four-quarter basis of not less than $22 million at March 31, 2017 and $25 million at the end of each fiscal quarter thereafter; and |
|
|
• |
ratio of restricted and unrestricted cash and marketable securities to workers’ compensation and safety incentive liabilities of at least 1.0:1.0, measured quarterly on a rolling four-quarter basis. |
The Agreement includes certain additional restrictions as follows:
|
|
• |
capital expenditures may not exceed a total of $4.0 million in 2016 without the Bank’s prior approval; |
|
|
• |
incurring additional indebtedness is prohibited without the prior approval of the Bank, other than purchase financing (including capital leases) for the acquisition of assets, provided that the aggregate of all purchase financing does not exceed $1,000,000 at any time; and |
|
|
• |
the Company may not terminate or cancel any of the AICE policies without the Bank’s prior written consent. |
The Agreement also contains other customary events of default. If an event of default under the Agreement occurs and is continuing, the Bank may declare any outstanding obligations under the Credit Agreement to be immediately due and payable.
At December 31, 2016, the Company was in violation of the capital expenditure limitation. The Bank agreed to waive this covenant violation.
The Company maintains a mortgage loan with the Bank with a balance of approximately $4.6 million and $4.8 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, secured by the Company’s corporate office building in Vancouver, Washington. This loan requires payment of
- 42 -
monthly principal payments of $18,375 plus interest at a rate of one month LIBOR plus 2.25%, with the unpaid principal balance due February 1, 2018.
Management expects that the funds anticipated to be generated from operations, current liquid assets, and availability under the Company’s revolving credit facility will be sufficient in the aggregate to fund the Company’s working capital needs for the next twelve months.
Contractual Obligations
The Company's contractual obligations as of December 31, 2016 are summarized below:
|
|
|
As of December 31, 2016 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Payments Due by Period |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
|
Less than |
|
|
1 - 3 |
|
|
4 - 5 |
|
|
After |
|
||||
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
1 year |
|
|
years |
|
|
years |
|
|
5 years |
|
|||||
|
Operating leases |
|
$ |
13,324 |
|
|
$ |
4,101 |
|
|
$ |
5,815 |
|
|
$ |
2,654 |
|
|
$ |
754 |
|
|
Long-term debt |
|
|
4,612 |
|
|
|
221 |
|
|
|
4,392 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
Total contractual obligations |
|
$ |
17,936 |
|
|
$ |
4,322 |
|
|
$ |
10,207 |
|
|
$ |
2,654 |
|
|
$ |
754 |
|
Inflation
Inflation generally has not been a significant factor in the Company's operations during the periods discussed above. The Company has taken into account the impact of escalating medical and other costs in establishing reserves for future expenses for workers' compensation claims.
The Company's exposure to market risk for changes in interest rates primarily relates to its investment portfolio of liquid assets and its outstanding borrowings on its line of credit and long-term debt. As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s investment portfolio consisted principally of approximately $286.5 million in money market funds, $10.8 million in certificates of deposit, $3.7 million in corporate bonds, $2.9 million in municipal bonds, and $0.8 million in U.S. treasuries. The Company’s outstanding long-term debt totaled approximately $4.6 million at December 31, 2016. Based on the Company's overall interest exposure at December 31, 2016, a 100 basis point increase in market interest rates would not have a material effect on the fair value of the Company's investment portfolio of liquid assets, its outstanding borrowings or its results of operations because of the predominantly short maturities of the securities within the investment portfolio and the relative size of the outstanding borrowings.
The consolidated financial statements and notes thereto required by this item begin on page F-1 of this report, as listed in Item 15.
None
- 43 -
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain “disclosure controls and procedures” that are designed with the objective of providing reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed in the reports we file or submit under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, our management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, and our management is required to apply their judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
The Company’s CEO and CFO have concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) were not effective as of December 31, 2016 because of the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting ("ICFR") described below. A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in ICFR such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement to the annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
Notwithstanding the material weaknesses in our ICFR described below, we have concluded that the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on
Form 10-K present fairly, in all material respects, our financial position, results of operations and cash flows for the periods presented in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our ICFR is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, our CEO and our CFO to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of our consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP. Management, with the participation of our CEO and CFO, conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our ICFR as of December 31, 2016. This evaluation was based on the framework established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based upon that evaluation, management has concluded that we did not maintain effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016 as a result of the following material weaknesses.
Information and Technology Controls
Management previously identified a material weakness in internal controls related to its information and technology systems (“IT systems”). Specifically, the Company did not maintain effective controls over user access to IT systems and changes to programs and data. While management has developed remediation plans with respect to the identified deficiencies, the remediation efforts, which include improvements to governance over IT controls, were not implemented in 2016. As a result of the deficiencies identified, there is a possibility that the
- 44 -
business process controls that are dependent on IT systems or electronic data and financial reports generated from such IT systems could be adversely affected.
Workers’ Compensation Expense
Management previously identified a material weakness in internal controls over the process for deriving accounting estimates related to workers’ compensation expense. Specifically, the Company did not ensure appropriate review of the data provided to its actuary.
Management has taken a number of actions and implemented controls in 2016 to remediate this deficiency, and management believes that these activities, in conjunction with other control activities that operated effectively during the year, will successfully remediate this material weakness. However, certain of these control activities were implemented or revised later in 2016, and management cannot conclude that the material weakness is remediated until the applicable controls have operated for a sufficient period of time to demonstrate operating effectiveness.
Attestation Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016 has been audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report included below.
Remediation Status and Plans
Information and Technology Controls
Management is taking a number of actions to remediate the material weakness related to IT controls, including but not limited to the following:
|
|
• |
Establishing a more rigorous review process over the evaluation of user access to IT systems, including preventative reviews during employment changes and periodic detective reviews. |
|
|
• |
Improving the structure and governance surrounding controls over IT systems. |
|
|
• |
Implementing enhanced review procedures and analysis over the segregation of duties in IT systems. |
|
|
• |
Improving the procedures and documentation associated with program change management, including implementing improved tools over system change logging. |
|
|
• |
Revising policies on the documentation of IT control performance and the retention of that documentation. |
|
|
• |
Replacing certain IT systems that have inherent control limitations. |
Management believes the measures described above will remediate the identified material weakness in future periods. Certain of these remediation efforts will require more time to execute than others, specifically the implementation of new systems and tools to address existing inherent control limitations. Assessing the effectiveness of internal control requires a period of repeatable execution, and therefore the successful remediation of this material weakness will depend on management’s ability to ensure timely and effective implementation of these systems and tools. In addition, management may determine it is necessary to take additional measures to address control deficiencies or to modify certain of the remediation
- 45 -
measures described above.
Workers’ Compensation Expense
Management believes that it has implemented control activities as of December 31, 2016 that address the material weakness related to workers’ compensation expense. Remediation of the material weakness is dependent on these control activities operating for a sufficient period of time to demonstrate operating effectiveness.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Significant progress has been made in remediating the material weaknesses identified in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2015. In addition to the progress described above, testing of both the design and operating effectiveness of new and improved controls was completed, and management concluded that the previously identified material weaknesses related to the Company’s control environment, review of journal entries, reconciliation of workers’ compensation accruals and review of payroll tax accruals have been successfully remediated at December 31, 2016. Actions taken in the year included but were not limited to the following:
|
|
• |
Terminated the employment of the former CFO following his report to the Audit Committee regarding his actions in recording unsupported journal entries in the Company’s financial records. |
|
|
• |
Engaged an independent public accounting firm to perform a forensic accounting investigation for the period from January 1, 2009, through March 31, 2016. |
|
|
• |
Hired a new permanent CFO, Controller and Assistant Controller with meaningful industry, public company accounting and financial experience. |
|
|
• |
In addition to the new accounting and finance leadership team noted above, increased and enhanced resources within the accounting and finance group to address standardization of processes, training regarding critical accounting policies affecting the Company and development of competencies and understanding of relevant accounting policies and ICFR. |
|
|
• |
Increased the number of positions on the Board of Directors from six to seven and appointed an individual with extensive financial management and public company experience to fill the vacancy. Having met all applicable financial literacy and independence requirements, this individual was appointed to serve as a member of the Audit Committee and as the Audit Committee financial expert. The Board of Directors further increased the number of Board positions to eight in January 2017 and appointed an individual with extensive industry and financial management experience to fill the new position. |
|
|
• |
Retained third-party experts to provide training for all accounting staff and other relevant personnel on the requirements and importance of ICFR, disclosure and financial records requirements of the federal securities laws applicable to public companies, and the requirements and significance of the Company’s Code of Ethics. |
|
|
• |
Implemented a process of regular communication by the Board of Directors, Audit Committee, and executive officers to all employees regarding the ethical values of the Company and the requirement on the part of all directors, officers, and employees to |
- 46 -
|
|
comply with applicable law, the Company’s Code of Business Conduct, and the Company's accounting policies and ICFR. |
|
|
• |
Established a Workers’ Compensation Committee (“WCC”) consisting of the Chief Operating Officer – Corporate Operations, Chief Financial Officer, Corporate Controller, Director of Insurance and a member of the Board of Directors to oversee the Company’s controls and procedures related to workers’ compensation claims administration and expense and its process for developing reserve estimates, as well as to participate in substantive communications with the Company’s independent actuary with regard to the Company’s reserve for workers’ compensation liabilities. |
|
|
• |
Established a procedure for quarterly meetings of the WCC with the Company’s independent actuary with the goal of ensuring that the actuary is fully informed and has a complete understanding of the components included in the payroll and workers’ compensation claims data provided to the actuary by the Company and to review fully the quarterly actuarial report produced by the actuary. Meetings occurred in April, July, and October 2016 and January 2017. |
|
|
• |
Enhanced our reconciliation of the data provided to the actuary, including increasing the scope of the data reconciled, improving the documentation of the reconciliation and agreeing data from the final issued actuary report to the original data sources. |
|
|
• |
Revised controls and implemented new controls over the recording of journal entries to ensure that manual journal entries recorded in the financial records are properly prepared, supported by adequate documentation, and independently reviewed and approved. |
|
|
• |
Revised controls and implemented new controls over the effective and timely reconciliation of balance sheet accounts, including enhancing the documentation and precision of reconciliations and ensuring proper review and approval of reconciliations. |
Other than the measures described above, there have been no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2016 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Inherent Limitations
Control systems, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control systems' objectives are being met. Further, the design of any control systems must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of all controls must be considered relative to their costs. Due to the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within our Company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of simple errors or mistakes. Control systems can also be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of controls is based in part on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or deterioration in the degree of compliance with policies or procedures.
- 47 -
Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer Certifications
The certifications of our CEO and CFO required under Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act have been filed as Exhibits 31.1 and 31.2 to this report.
- 48 -
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Barrett Business Services, Inc.,
Vancouver, Washington
We have audited Barrett Business Services, Inc. (the "Company's") internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company's management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Report over Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company's principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company's board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the
- 49 -
company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The following material weaknesses have been identified and included in management's assessment:
|
|
• |
In the course of completing their assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, management identified a number of recurring deficiencies from the prior year related to the design and operating effectiveness of information technology (“IT”) general controls for information systems that comprise part of the Company’s system of internal control over financial reporting and are relevant to the preparation of its consolidated financial statements (such information technology systems are referred to as the “affected IT systems”). The controls over user access were not designed and operating effectively to prevent or detect inappropriate access to the affected IT systems. The controls over change management were not designed and operating effectively to ensure that changes to the affected IT systems were identified, authorized, tested and implemented appropriately which include governance over IT general controls. As a result of the deficiencies identified, there is a possibility that the business process controls, which are dependent on IT systems, or electronic data and financial reports generated from such IT systems, could be adversely affected. |
|
|
• |
Management previously identified a material weakness in internal controls over the process for deriving accounting estimates related to workers’ compensation expense. Specifically, the Company did not ensure appropriate review of the data provided to its actuary. Management has taken a number of actions and implemented controls in 2016 to remediate this deficiency. However, certain of these control activities were implemented or revised later in 2016, and management cannot conclude that the material weakness is remediated until the applicable controls have operated for a sufficient period of time to demonstrate that these controls are operating effectively. |
These material weaknesses were considered in determining the nature, timing, and extent of audit tests applied in our audit of the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2016, of the Company and this report does not affect our report on such financial statements.
In our opinion, because of the effect of the material weaknesses identified above on the achievement of the objectives of the control criteria, the Company has not maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on the criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements of Barrett Business Services, Inc. as of and for the year ended December 31, 2016, and our report dated March 8, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Portland, Oregon
March 8, 2017
- 50 -
None.
- 51 -
Information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the information set forth under the captions "Election of Directors," "Stock Ownership by Principal Stockholders and Management--Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance," “Executive Officers” and "Code of Ethics." in our definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this report (the “Proxy Statement”).
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the information set forth under the captions “Director Compensation for 2016” and “Executive Compensation” in the Proxy Statement.
|
Item 12. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the information set forth under the caption "Stock Ownership of Principal Stockholders and Management – Beneficial Ownership Table" and “Additional Equity Compensation Plan Information” in the Proxy Statement.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the information set forth under the caption "Election of Directors" and "Related Person Transactions" in the Proxy Statement.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the information set forth under the caption "Matters Relating to Our Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in the Proxy Statement.
- 52 -
Financial Statements and Schedules
The Financial Statements, together with the report thereon of Deloitte & Touche LLP and Moss Adams LLP, are included on the pages indicated below:
No schedules are required to be filed herewith.
Exhibits
Exhibits are listed in the Exhibit Index that follows the signature page of this report.
- 53 -
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Barrett Business Services, Inc.,
Vancouver, Washington
We have audited the accompanying consolidated Balance Sheet of Barrett Business Services, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2016, and the related consolidated Statements of Operations, Comprehensive Income (Loss), Stockholders’ Equity, and Cash Flows for the year then ended. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall consolidated financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Barrett Business Services, Inc. as of December 31, 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on the criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated March 8, 2017 expressed an adverse opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting because of the material weaknesses.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Portland, Oregon
March 8, 2017
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Barrett Business Services, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2015 and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2015. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall consolidated financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Barrett Business Services, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2015 and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash flows for the each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2015, in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America.
/s/ Moss Adams LLP
Portland, Oregon
May 25, 2016
F-2
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
December 31, 2016 and 2015
(In Thousands, Except Par Value)
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
50,768 |
|
|
$ |
25,218 |
|
|
Trade accounts receivable, net |
|
|
126,484 |
|
|
|
90,529 |
|
|
Income taxes receivable |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,038 |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other |
|
|
3,899 |
|
|
|
3,173 |
|
|
Investments |
|
|
5,675 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Restricted cash and investments |
|
|
48,557 |
|
|
|
86,110 |
|
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
25,242 |
|
|
|
20,941 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
260,625 |
|
|
|
227,009 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investments |
|
|
642 |
|
|
|
6,082 |
|
|
Property, equipment and software, net |
|
|
26,673 |
|
|
|
22,820 |
|
|
Restricted cash and investments |
|
|
252,707 |
|
|
|
187,916 |
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
47,820 |
|
|
|
47,820 |
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
9,293 |
|
|
|
5,130 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
597,760 |
|
|
$ |
496,777 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current portion of long-term debt |
|
$ |
221 |
|
|
$ |
19,833 |
|
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
4,944 |
|
|
|
3,217 |
|
|
Accrued payroll, payroll taxes and related benefits |
|
|
153,110 |
|
|
|
121,343 |
|
|
Income taxes payable |
|
|
3,041 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other accrued liabilities |
|
|
7,674 |
|
|
|
6,166 |
|
|
Workers' compensation claims liabilities |
|
|
81,339 |
|
|
|
65,581 |
|
|
Safety incentives liability |
|
|
24,835 |
|
|
|
21,253 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
275,164 |
|
|
|
237,393 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term workers' compensation claims liabilities |
|
|
231,198 |
|
|
|
190,094 |
|
|
Long-term debt |
|
|
4,392 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
15,872 |
|
|
|
13,256 |
|
|
Customer deposits and other long-term liabilities |
|
|
1,441 |
|
|
|
1,483 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
528,067 |
|
|
|
442,226 |
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (Notes 6, 8 and 12) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders' equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, $.01 par value; 20,500 shares authorized, 7,244 and 7,203 shares issued and outstanding |
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
72 |
|
|
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
9,638 |
|
|
|
6,964 |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
(3 |
) |
|
|
(31 |
) |
|
Retained earnings |
|
|
59,986 |
|
|
|
47,546 |
|
|
|
|
|
69,693 |
|
|
|
54,551 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
597,760 |
|
|
$ |
496,777 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-3
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
(In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts)
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Professional employer service fees |
|
$ |
673,924 |
|
|
$ |
572,286 |
|
|
$ |
470,522 |
|
|
Staffing services |
|
|
166,662 |
|
|
|
168,555 |
|
|
|
165,833 |
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
840,586 |
|
|
|
740,841 |
|
|
|
636,355 |
|
|
Cost of revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct payroll costs |
|
|
126,753 |
|
|
|
127,964 |
|
|
|
126,399 |
|
|
Payroll taxes and benefits |
|
|
357,867 |
|
|
|
312,284 |
|
|
|
263,100 |
|
|
Workers' compensation |
|
|
210,430 |
|
|
|
171,137 |
|
|
|
213,451 |
|
|
Total cost of revenues |
|
|
695,050 |
|
|
|
611,385 |
|
|
|
602,950 |
|
|
Gross margin |
|
|
145,536 |
|
|
|
129,456 |
|
|
|
33,405 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
|
|
113,342 |
|
|
|
90,177 |
|
|
|
74,065 |
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
3,253 |
|
|
|
2,851 |
|
|
|
2,506 |
|
|
Income (loss) from operations |
|
|
28,941 |
|
|
|
36,428 |
|
|
|
(43,166 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other (expense) income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investment income, net |
|
|
956 |
|
|
|
771 |
|
|
|
543 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
|
(807 |
) |
|
|
(1,965 |
) |
|
|
(173 |
) |
|
Loss on litigation |
|
|
(3,544 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other, net |
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
(88 |
) |
|
|
152 |
|
|
Other (expense) income, net |
|
|
(3,355 |
) |
|
|
(1,282 |
) |
|
|
522 |
|
|
Income (loss) before income taxes |
|
|
25,586 |
|
|
|
35,146 |
|
|
|
(42,644 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
|
|
6,787 |
|
|
|
9,652 |
|
|
|
(17,098 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
18,799 |
|
|
$ |
25,494 |
|
|
$ |
(25,546 |
) |
|
Basic earnings (loss) per common share |
|
$ |
2.60 |
|
|
$ |
3.55 |
|
|
$ |
(3.57 |
) |
|
Weighted average number of basic common shares outstanding |
|
|
7,226 |
|
|
|
7,173 |
|
|
|
7,160 |
|
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per common share |
|
$ |
2.55 |
|
|
$ |
3.47 |
|
|
$ |
(3.57 |
) |
|
Weighted average number of diluted common shares outstanding |
|
|
7,378 |
|
|
|
7,353 |
|
|
|
7,160 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
(In Thousands)
|
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
18,799 |
|
|
$ |
25,494 |
|
|
$ |
(25,546 |
) |
|
Unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities, net of tax of $19, ($8), and $3 in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively |
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
(8 |
) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
Comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
18,827 |
|
|
$ |
25,486 |
|
|
$ |
(25,543 |
) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity
Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
(In Thousands)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Comprehensive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Paid-in |
|
|
(Loss) |
|
|
Retained |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Income |
|
|
Earnings |
|
|
Total |
|
||||||
|
Balance, December 31, 2013 |
|
|
7,165 |
|
|
$ |
72 |
|
|
$ |
5,781 |
|
|
$ |
(26 |
) |
|
$ |
59,351 |
|
|
$ |
65,178 |
|
|
Common stock issued on exercise of options |
|
|
56 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
434 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
434 |
|
|
Common stock repurchased on vesting of restricted stock units |
|
|
(8 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(407 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(407 |
) |
|
Share based compensation expense, net of tax |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,699 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,699 |
|
|
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
578 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
578 |
|
|
Company repurchase of common stock |
|
|
(87 |
) |
|
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
(3,675 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3,676 |
) |
|
Cash dividends on common stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,443 |
) |
|
|
(5,443 |
) |
|
Unrealized holding gains on investments, net of tax |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(25,546 |
) |
|
|
(25,546 |
) |
|
Balance, December 31, 2014 |
|
|
7,126 |
|
|
$ |
71 |
|
|
$ |
4,410 |
|
|
$ |
(23 |
) |
|
$ |
28,362 |
|
|
$ |
32,820 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock issued on exercise of options |
|
|
89 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
701 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
702 |
|
|
Common stock repurchased on vesting of restricted stock units |
|
|
(12 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(465 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(465 |
) |
|
Share based compensation expense, net of tax |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,386 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,386 |
|
|
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(68 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(68 |
) |
|
Company repurchase of common stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Cash dividends on common stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(6,310 |
) |
|
|
(6,310 |
) |
|
Unrealized holding loss on investments, net of tax |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(8 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(8 |
) |
|
Net income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
25,494 |
|
|
|
25,494 |
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2015 |
|
|
7,203 |
|
|
$ |
72 |
|
|
$ |
6,964 |
|
|
$ |
(31 |
) |
|
$ |
47,546 |
|
|
$ |
54,551 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock issued on exercise of options |
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
72 |
|
|
Common stock repurchased on vesting of restricted stock units |
|
|
(11 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(433 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(433 |
) |
|
Share based compensation expense, net of tax |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,782 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,782 |
|
|
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
253 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
253 |
|
|
Company repurchase of common stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Cash dividends on common stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(6,359 |
) |
|
|
(6,359 |
) |
|
Unrealized holding gains on investments, net of tax |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
Net income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
18,799 |
|
|
|
18,799 |
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2016 |
|
|
7,244 |
|
|
$ |
72 |
|
|
$ |
9,638 |
|
|
$ |
(3 |
) |
|
$ |
59,986 |
|
|
$ |
69,693 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
(In Thousands)
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Cash flows from operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) |
|
$ |
18,799 |
|
|
$ |
25,494 |
|
|
$ |
(25,546 |
) |
|
Reconciliations of net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
3,253 |
|
|
|
2,851 |
|
|
|
2,506 |
|
|
(Gains) losses recognized on investments |
|
|
(3 |
) |
|
|
(2 |
) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
Loss recognized on sale of property |
|
|
31 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
||
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
(1,704 |
) |
|
|
2,728 |
|
|
|
(9,792 |
) |
|
Share-based compensation |
|
|
2,782 |
|
|
|
2,386 |
|
|
|
1,699 |
|
|
Excess tax from share-based compensation |
|
|
(253 |
) |
|
|
68 |
|
|
|
(578 |
) |
|
Changes in certain assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade accounts receivable, net |
|
|
(35,955 |
) |
|
|
12,097 |
|
|
|
(17,041 |
) |
|
Income taxes receivable |
|
|
1,038 |
|
|
|
10,521 |
|
|
|
(11,421 |
) |
|
Prepaid expenses and other |
|
|
(726 |
) |
|
|
640 |
|
|
|
(387 |
) |
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
1,727 |
|
|
|
498 |
|
|
|
(533 |
) |
|
Accrued payroll, payroll taxes and related benefits |
|
|
31,767 |
|
|
|
5,506 |
|
|
|
21,950 |
|
|
Other accrued liabilities |
|
|
1,508 |
|
|
|
(64 |
) |
|
|
3,893 |
|
|
Income taxes payable |
|
|
3,294 |
|
|
|
506 |
|
|
|
411 |
|
|
Workers' compensation claims liabilities |
|
|
51,235 |
|
|
|
30,397 |
|
|
|
104,223 |
|
|
Safety incentives liability |
|
|
3,582 |
|
|
|
7,021 |
|
|
|
1,146 |
|
|
Customer deposits, long-term liabilities and other assets, net |
|
|
(68 |
) |
|
|
(16 |
) |
|
|
(937 |
) |
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
80,307 |
|
|
|
100,631 |
|
|
|
69,596 |
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase of equipment and software |
|
|
(7,106 |
) |
|
|
(2,996 |
) |
|
|
(4,632 |
) |
|
Proceeds from sale of property |
|
|
1,459 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
||
|
Purchase of investments |
|
|
(264 |
) |
|
|
(8,214 |
) |
|
|
(38,434 |
) |
|
Proceeds from sales and maturities of investments |
|
|
4,796 |
|
|
|
52,996 |
|
|
|
13,241 |
|
|
Purchase of restricted cash and investments |
|
|
(185,845 |
) |
|
|
(336,083 |
) |
|
|
(163,174 |
) |
|
Proceeds from sales and maturities of restricted cash and investments |
|
|
153,890 |
|
|
|
238,701 |
|
|
|
10,524 |
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(33,070 |
) |
|
|
(55,596 |
) |
|
|
(182,475 |
) |
|
Cash flows from financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from credit-line borrowings |
|
|
14,868 |
|
|
|
46,106 |
|
|
|
6,242 |
|
|
Payments on credit-line borrowings |
|
|
(14,868 |
) |
|
|
(46,106 |
) |
|
|
(6,242 |
) |
|
Proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
40,000 |
|
|
|
Commitment fee from the issuance of long-term debt |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(400 |
) |
|
|
Payments on long-term debt |
|
|
(15,220 |
) |
|
|
(25,220 |
) |
|
|
(220 |
) |
|
Repurchase of common stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3,676 |
) |
|
|
Common stock repurchased on vesting of restricted stock units |
|
|
(433 |
) |
|
|
(465 |
) |
|
|
(407 |
) |
|
Dividends paid |
|
|
(6,359 |
) |
|
|
(6,310 |
) |
|
|
(5,443 |
) |
|
Proceeds from the exercise of stock options |
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
702 |
|
|
|
434 |
|
|
Excess tax benefit from share-based compensation |
|
|
253 |
|
|
|
(68 |
) |
|
|
578 |
|
|
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities |
|
|
(21,687 |
) |
|
|
(31,361 |
) |
|
|
30,866 |
|
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
25,550 |
|
|
|
13,674 |
|
|
|
(82,013 |
) |
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year |
|
|
25,218 |
|
|
|
11,544 |
|
|
|
93,557 |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of year |
|
$ |
50,768 |
|
|
$ |
25,218 |
|
|
$ |
11,544 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-7
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
1. |
Summary of Operations and Significant Accounting Policies |
Nature of operations
Barrett Business Services, Inc. (“BBSI” or the “Company”), is a leading provider of business management solutions for small and mid-sized companies. The Company has developed a management platform that integrates a knowledge-based approach from the management consulting industry with tools from the human resource outsourcing industry. This platform, through the effective leveraging of human capital, helps our business owner clients run their businesses more effectively.
We believe this platform, delivered through our decentralized organizational structure, differentiates BBSI from our competitors. The Company operates through a network of 57 branch offices throughout California, Oregon, Utah, Washington, Idaho, Arizona, Colorado, Maryland, North Carolina, Delaware, Nevada, Pennsylvania and Virginia. Approximately 78%, 78% and 77%, respectively, of our revenue during 2016, 2015 and 2014 was attributable to our California operations. BBSI was incorporated in Maryland in 1965.
The Company operates a wholly owned captive insurance company, Associated Insurance Company for Excess ("AICE"). AICE is a fully licensed captive insurance company holding a certificate of authority from the Arizona Department of Insurance. The purpose of AICE is twofold: (1) to provide access to more competitive and cost effective insurance markets and (2) to provide additional flexibility in cost effective risk management. AICE provides to the Company excess workers' compensation coverage up to $5.0 million per occurrence, except in Maryland and Colorado, where our retention per occurrence is $1.0 million and $2.0 million, respectively. AICE maintains excess workers’ compensation insurance coverage with Chubb Limited (“Chubb”, formerly ACE Group) between $5.0 million and $15.0 million per occurrence, except in Maryland, where coverage with Chubb is between $1.0 million and $25.0 million per occurrence, and in Colorado, where the coverage with Chubb is between $2.0 million and statutory limits per occurrence.
The Company also operates a wholly owned insurance company, Ecole Insurance Company (“Ecole”). Ecole is a fully licensed insurance company holding a certificate of authority from the Arizona Department of Insurance. Ecole provides workers’ compensation coverage to the Company’s employees working in Arizona, Utah and Nevada.
Principles of consolidation
The accompanying financial statements are prepared on a consolidated basis. All intercompany account balances and transactions between BBSI, AICE, Ecole and BBS I, LLC, the aircraft subsidiary which owns an aircraft for management’s operational travel needs, have been eliminated in consolidation.
Reportable segment
The Company has one operating and reporting segment. The chief operating decision maker (our Chief Executive Officer) regularly reviews the financial information of our business at a consolidated level in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance.
F-8
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Revenue recognition
We recognize professional employer (“PEO”) service and staffing service revenue as services are rendered by our workforce. PEO services are normally used by organizations to satisfy ongoing needs related to the management of human capital and are governed by the terms of a client services agreement which covers all employees at a particular work site. Our client services agreements have a minimum term of one year, are renewable on an annual basis and typically require 30 days’ written notice to cancel or terminate the contract by either party. In addition, our client services agreements provide for immediate termination upon any default of the client regardless of when notice is given.
We report PEO revenues on a net basis because we are not the primary obligor for certain of the services provided to our clients on behalf of their employees pursuant to our client services agreements. Specifically, we present revenue net of the amounts received or billed for direct payroll expenses such as salaries, wages, health insurance, and employee out-of-pocket expenses incurred incidental to employment. Safety incentive costs are also netted against PEO service revenue in our consolidated statements of operations. Safety incentives represent cash incentives paid to certain client companies for maintaining safe-work practices and minimizing workplace injuries. The safety incentive is based on a percentage of annual payroll and is paid annually to clients who meet predetermined workers' compensation claims cost objectives.
Cost of revenues
Our cost of revenues for PEO services includes employer payroll-related taxes and workers' compensation costs. Our cost of revenues for staffing services includes direct payroll costs, employer payroll-related taxes, employee benefits, and workers’ compensation costs. Direct payroll costs represent the gross payroll earned by staffing services employees based on salary or hourly wages. Payroll taxes and employee benefits consist of the employer's portion of Social Security and Medicare taxes, federal and state unemployment taxes, and staffing services employee reimbursements for materials, supplies and other expenses, which are paid by our customer. Workers' compensation costs consist primarily of the costs associated with our workers' compensation program, including claims reserves, claims administration fees, legal fees, medical cost containment (“MCC”) expense, state administrative agency fees, third-party broker commissions, risk manager payroll, premiums for excess insurance, the fronted insurance program and costs associated with operating our two wholly owned, fully licensed insurance companies, AICE and Ecole.
Cash and cash equivalents
We consider non-restricted short-term investments, which are highly liquid, readily convertible into cash, and have maturities at acquisition of less than three months to be cash equivalents for purposes of the consolidated statements of cash flows and consolidated balance sheets. The Company maintains cash balances in bank accounts that normally exceed FDIC insured limits. The Company has not experienced any losses related to its cash concentration.
Investments
As of December 31, 2016, the Company's investments consisted of certificates of deposit, corporate bonds and municipal bonds. We classify our investments as trading or available-for-sale. The Company had no trading securities at December 31, 2016 and 2015. The Company classifies certificates of deposit, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds as
F-9
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
available for sale. They are reported at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of taxes, shown as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in stockholders' equity. Management considers available evidence in evaluating potential impairment of investments, including the duration and extent to which fair value is less than cost. Realized gains and losses on sales of investments are included in other income (expense) as other, net in our consolidated statements of operations. In the event a loss is determined to be other-than-temporary, the loss will be recognized in the consolidated statements of operations.
Restricted cash and investments
At December 31, 2016, restricted cash and investments consisted of restricted cash, money market funds, certificates of deposit, corporate bonds, municipal bonds with maturities generally from 180 days to two years, and U.S. Treasuries. At December 31, 2016, the approximate fair value of restricted cash and investments equaled their approximate amortized cost. Restricted investments have been categorized as available-for-sale. They are reported at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of taxes, shown as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in stockholders’ equity. Management considers available evidence in evaluating potential impairment of restricted investments, including the duration and extent to which fair value is less than cost. Realized gains and losses on sales of restricted investments are included in other income (expense) as other, net in our consolidated statements of operations. In the event a loss is determined to be other-than-temporary, the loss will be recognized in the consolidated statements of operations.
Allowance for doubtful accounts
We make estimates of the collectability of our accounts receivable for services provided to our customers. Management analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit-worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customers' payment trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts. If the financial condition of our customers deteriorates resulting in an impairment of their ability to make payments, additional allowances may be required.
Our allowance for doubtful accounts activity is summarized as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Balance at January 1, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts |
|
$ |
268 |
|
|
$ |
291 |
|
|
$ |
242 |
|
|
Charges to expense |
|
|
(115 |
) |
|
|
116 |
|
|
|
103 |
|
|
Write-offs of uncollectible accounts, net of recoveries |
|
|
(75 |
) |
|
|
(139 |
) |
|
|
(54 |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts |
|
$ |
78 |
|
|
$ |
268 |
|
|
$ |
291 |
|
Income taxes
Our income taxes are accounted for using an asset and liability approach. This requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities at the applicable tax rates. A valuation allowance is recorded against deferred tax assets if, based on the weight of the available evidence, it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The factors used to assess the likelihood of realization include the Company’s forecast of the reversal of temporary
F-10
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
differences, future taxable income and available tax planning strategies that could be implemented to realize the net deferred tax assets. Failure to achieve forecasted taxable income in applicable tax jurisdictions could affect the ultimate realization of deferred tax assets and could result in an increase in the Company’s effective tax rate on future earnings.
The determination of our provision for income taxes requires significant judgment, the use of estimates, and the interpretation and application of complex tax laws. Significant judgment is required in assessing the timing and amounts of deductible and taxable items and the probability of sustaining uncertain tax positions. The Company recognizes the tax benefit from uncertain tax positions if it is more likely than not that the tax positions will be sustained on examination by the tax authorities. The tax benefit is measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. As facts and circumstances change, we reassess these probabilities and record any changes in the consolidated financial statements as appropriate. The Company recognizes interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
Goodwill and intangible assets
Goodwill is recorded as the difference, if any, between the aggregate consideration paid for a business combination and the fair value of the net assets acquired. Goodwill is not amortized but is evaluated for impairment annually, or more frequently if circumstances indicate that it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is below its carrying value. The Company has one reporting unit and evaluates the carrying value of goodwill annually at December 31. No impairment has been recognized in the periods presented.
Property, equipment and software
Property, equipment and software are stated at cost. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to selling, general and administrative expenses as incurred and expenditures for additions and improvements are capitalized. The cost of assets sold or otherwise disposed of and the related accumulated depreciation are eliminated from the accounts, and any resulting gain or loss is reflected in the consolidated statements of operations.
Depreciation of property, equipment and software is calculated using either straight-line or accelerated methods over estimated useful lives of the related assets or lease terms, as follows:
|
|
|
Years |
|
Buildings |
|
39 |
|
Office furniture and fixtures |
|
7 |
|
Computer hardware and software |
|
3-10 |
|
Aircraft |
|
20 |
|
Automobile |
|
5 |
|
Leasehold improvements |
|
Shorter of lease term or estimated useful life |
Impairment of long-lived assets
Long-lived assets, such as property, equipment and software and acquired intangibles subject to amortization, are reviewed for impairment annually, or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the remaining estimated useful life may warrant
F-11
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
revision or that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Some of the events or changes in circumstances that would trigger an impairment review include, but are not limited to, significant under-performance relative to expected and/or historical results, significant negative industry or economic trends or knowledge of transactions involving the sale of similar property at amounts below the carrying value.
Assets are grouped for measurement of impairment at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent of the cash flows of other assets. If the carrying amount of an asset group exceeds the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset group, then an impairment charge is recognized to the extent the carrying amount exceeds the asset group’s fair value. In determining fair value, management considers current results, trends, future prospects, and other economic factors. No impairment has been recognized in the periods presented.
Leases
The Company leases office facilities and equipment under operating leases. For significant lease agreements that provide for escalating rent payments or free-rent occupancy periods, the Company recognizes rent expense on a straight-line basis over the non-cancelable lease term. Deferred rent is included in other accrued liabilities and customer deposits and other long-term liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets.
Workers’ compensation claims liabilities
Our workers’ compensation claims liabilities do not represent an exact calculation of liability but rather management’s best estimate, utilizing actuarial expertise and projection techniques, at a given reporting date. The estimated liability for open workers’ compensation claims is based on an evaluation of information provided by our internal claims adjusters and our third-party administrators for workers’ compensation claims, coupled with an actuarial estimate of future adverse loss development with respect to reported claims and incurred but not reported claims (together, “IBNR”). At December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, workers' compensation claims liabilities included case reserve estimates for reported losses, plus additional amounts for estimated IBNR claims, MCC and legal costs, and unallocated loss adjustment expenses, including future administrative fees to be paid to third-party service providers. These estimates are reviewed at least quarterly and adjustments to estimated liabilities are reflected in current operating results as they become known.
The process of arriving at an estimate of unpaid claims and claims adjustment expense involves a high degree of judgment and is affected by both internal and external events, including changes in claims handling practices, changes in reserve estimation procedures, changes in individuals involved in the reserve estimation process, inflation, trends in the litigation and settlement of pending claims, and legislative changes.
Our estimates are based on informed judgment, derived from individual experience and expertise applied to multiple sets of data and analyses. We consider significant facts and circumstances known both at the time that loss reserves are initially established and as new facts and circumstances become known. Due to the inherent uncertainty underlying loss reserve estimates, the expenses incurred through final resolution of our liability for our workers’ compensation claims will likely vary from the related loss reserves at the reporting date. Therefore, as specific claims are paid out in the future, actual paid losses may be materially different from our current loss reserves.
F-12
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The Company’s independent actuary provides management with an estimate of the current and long-term portions of our total workers’ compensation claims, which is an important factor in our process for estimating workers' compensation claims liabilities. The current portion represents the independent actuary’s best estimate of payments the Company will make related to workers’ compensation claims over the ensuing twelve months.
A basic premise in most actuarial analyses is that historical data and past patterns demonstrated in the incurred and paid historical data form a reasonable basis upon which to project future outcomes, absent a material change. Significant structural changes to the available data can materially impact the reserve estimation process. To the extent a material change affecting the ultimate claim liability becomes known, such change is quantified to the extent possible through an analysis of internal Company data and, if available and when appropriate, external data. Nonetheless, actuaries exercise a considerable degree of judgment in the evaluation of these factors and the need for such actuarial judgment is more pronounced when faced with material uncertainties.
Safety incentives liability
Safety incentives represent cash incentives paid to certain PEO client companies for maintaining safe-work practices and minimizing workplace injuries. The incentive is based on a percentage of annual payroll and is paid annually to customers who meet predetermined workers’ compensation claims cost objectives. Safety incentive payments are made only after closure of all workers' compensation claims incurred during the customer’s contract period. The safety incentive liability is estimated and accrued each month based upon contract year-to-date payroll and the then current amount of the customer’s estimated workers’ compensation claims reserves as established by us and our third party administrator and the expected payout as determined by historical incentive payment trends. The Company provided $24.8 million and $21.3 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, as an estimate of the liability for unpaid safety incentives.
Customer deposits
We require deposits from certain PEO customers to cover a portion of our accounts receivable due from such customers in the event of default of payment.
Comprehensive income (loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) includes all changes in equity during a period except those that resulted from investments by or distributions to the Company's stockholders.
Other comprehensive income (loss) refers to revenues, expenses, gains and losses that under U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) are included in comprehensive income (loss), but excluded from net income (loss) as these amounts are recorded directly as an adjustment to stockholders' equity. Our other comprehensive income (loss) comprises unrealized holding gains and losses on our available for sale investments.
Statements of cash flows
Interest paid during 2016, 2015 and 2014 did not differ materially from interest expense. Income taxes paid (received) by the Company totaled $4.2 million, ($4.1) million and $3.3 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
F-13
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Basic and diluted earnings per share
Basic earnings per share are computed based on the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for each year using the treasury method. Diluted earnings per share reflect the potential effects of the exercise of outstanding stock options and the issuance of stock associated with outstanding restricted stock units. Basic and diluted shares outstanding are summarized as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Weighted average number of basic shares outstanding |
|
|
7,226 |
|
|
|
7,173 |
|
|
|
7,160 |
|
|
Effect of dilutive securities |
|
|
152 |
|
|
|
180 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Weighted average number of diluted shares outstanding |
|
|
7,378 |
|
|
|
7,353 |
|
|
|
7,160 |
|
As a result of the net loss for the year ended December 31, 2014, 227,000 potential common shares have been excluded from the calculation of diluted loss per share because their effect would be anti-dilutive.
Reclassifications
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation. Such reclassifications had no impact on the Company’s financial condition, operating results, cash flows, working capital or stockholders’ equity.
Accounting estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Estimates are used for fair value measurement of investments, allowance for doubtful accounts, deferred income taxes, carrying values for goodwill and property and equipment, accrued workers' compensation liabilities and safety incentive liabilities. Actual results may or may not differ from such estimates.
Recent accounting pronouncements
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The core principle of the update is that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which an entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The update also requires disclosure of sufficient information to enable users of financial statements to understand the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from contracts with customers.
In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-14, Revenue from Contracts with Customers: Deferral of the Effective Date. The update defers the effective date of ASU
F-14
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
2014-09 by one year, requiring public business entities to apply the guidance in ASU 2014-09 to annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period.
In March, April and May 2016, the FASB issued the following ASUs: ASU No. 2016-08, Principal versus Agent Considerations - Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net; ASU No. 2016-10, Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing; and ASU No. 2016-12, Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients. The amendments in these updates do not change the core principles of the guidance in ASU 2014-09. The effective date and transition requirements for these updates are the same as the effective date and transition requirements in ASU 2015-14. The Company is currently evaluating the impact on its consolidated financial statements and footnote disclosures of ASU 2014-09 and all related ASUs.
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes. The amendments in this update simplify the presentation of deferred income taxes by requiring that deferred tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent on the consolidated balance sheets. The amendments in this update are effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. The adoption of this standard will result in a current to noncurrent adjustment to the Company’s current deferred tax asset balance, which was $25.2 million at December 31, 2016. The Company will adopt this standard in the first interim period for the year ending December 31, 2017.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases. The core principle is that a lessee should recognize the assets and liabilities that arise from leases, including operating leases. Under the new guidance, a lessee should recognize in the statement of financial position a liability to make lease payments (the lease liability) and a right-of-use asset representing its right to use the underlying asset for the lease term. For leases with a term of 12 months or less, a lessee is permitted to make an accounting policy election by class of underlying asset not to recognize lease assets and lease liabilities. The recognition, measurement, and presentation of expenses and cash flows arising from a lease by a lessee have not significantly changed from previous GAAP. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the standard and the impact on its consolidated financial statements and footnote disclosures.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-09, Compensation – Stock Compensation. The amendments in this update simplify several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, and classification on the statement of cash flows. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the standard and the impact on its consolidated financial statements and footnote disclosures.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows: Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments. The amendments in this update provide guidance on eight specific cash flow issues that are not addressed by current GAAP. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is
F-15
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
currently evaluating the standard and the impact on its consolidated financial statements and footnote disclosures.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows: Restricted Cash. The amendments in this update require that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents. Therefore, amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents should be included with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning-of-period and end-of-period total amounts shown on the statement of cash flows. The amendments in this update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the standard and the impact on its consolidated financial statements and footnote disclosures.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-04, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other: Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment. The amendments in this update simplify how an entity is required to test goodwill for impairment by eliminating Step 2 from the goodwill impairment test. Step 2 measures a goodwill impairment loss by comparing the implied fair value of a reporting unit’s goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. The amendments in this update are effective for annual or any interim goodwill impairment tests in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019. The Company is currently evaluating the standard but does not expect it to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements or footnote disclosures.
|
2. |
Concentration of Credit Risk |
Financial instruments that potentially subject us to concentration of credit risk consist primarily of cash equivalents, investments, restricted cash and investments, and trade accounts receivable. We limit investment of cash equivalents and investments to financial institutions with high credit ratings. Credit risk on trade accounts is minimized as a result of the large and diverse nature of our customer base.
At December 31, 2016, we had concentrations of credit risk as follows:
|
|
• |
$286.5 million, at fair value, in money market funds. |
|
|
• |
$10.8 million, at fair value, in certificates of deposit. |
|
3. |
Fair Value Measurement |
Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
All of our financial instruments are recognized in our consolidated balance sheets. Carrying values approximate fair value of most financial assets and liabilities. Investments and restricted cash and investments are recorded at market value. The interest rates on our investments approximate current market rates for these types of investments.
In determining the fair value of our financial assets, the Company predominately uses the market approach. In determining the fair value of all its money market funds, certificates of deposit, municipal bonds, corporate bonds, and U.S. treasury bills, the Company utilizes non-binding quotes provided by our investment brokers.
F-16
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Factors used in determining the fair value of our financial assets and liabilities are summarized into three levels as established in the fair value hierarchy framework. The three levels of the fair value hierarchy are described below.
Level 1 – Inputs to the valuation methodology are unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2 – Inputs to the valuation methodology include:
|
|
• |
Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; |
|
|
• |
Quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in inactive markets; |
|
|
• |
Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability; |
|
|
• |
Inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means. |
Level 3 - Inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
In determining the fair value measurement of our financial assets, the fair value measurement level within the hierarchy is based on the lowest level input and is applied to each financial asset. Valuation techniques are used to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs.
The following table summarizes the Company’s investments at December 31, 2016 and 2015 measured at fair value on a recurring basis (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gains |
|
|
Recorded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gains |
|
|
Recorded |
|
||||
|
|
|
Cost |
|
|
(Losses) |
|
|
Basis |
|
|
Cost |
|
|
(Losses) |
|
|
Basis |
|
||||||
|
Current: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash equivalents: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Money market funds |
|
$ |
1,943 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
1,943 |
|
|
$ |
21,312 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
21,312 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Certificates of deposit |
|
$ |
4,737 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
4,737 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Municipal bonds |
|
|
713 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
714 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Corporate bonds |
|
|
225 |
|
|
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
224 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Restricted cash and investments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Money market funds |
|
$ |
48,557 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
48,557 |
|
|
$ |
76,023 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
76,023 |
|
|
Certificates of deposit |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
Total current investments |
|
$ |
56,175 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
56,175 |
|
|
$ |
107,335 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
107,335 |
|
F-17
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gains |
|
|
Recorded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gains |
|
|
Recorded |
|
||||
|
|
|
Cost |
|
|
(Losses) |
|
|
Basis |
|
|
Cost |
|
|
(Losses) |
|
|
Basis |
|
||||||
|
Long term: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Corporate bonds |
|
$ |
567 |
|
|
$ |
(1 |
) |
|
$ |
566 |
|
|
$ |
2,970 |
|
|
$ |
(24 |
) |
|
$ |
2,946 |
|
|
Municipal bonds |
|
|
76 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
76 |
|
|
|
3,135 |
|
|
|
(3 |
) |
|
|
3,132 |
|
|
Money market funds |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Restricted cash and investments (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Money market funds |
|
$ |
236,036 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
236,036 |
|
|
$ |
175,869 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
175,869 |
|
|
Certificates of deposit |
|
|
6,047 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,047 |
|
|
|
496 |
|
|
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
495 |
|
|
Corporate bonds |
|
|
2,886 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2,888 |
|
|
|
2,996 |
|
|
|
(24 |
) |
|
|
2,972 |
|
|
Municipal bonds |
|
|
2,069 |
|
|
|
(6 |
) |
|
|
2,063 |
|
|
|
3,613 |
|
|
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
3,612 |
|
|
U.S. treasuries |
|
|
834 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
834 |
|
|
|
4,752 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
4,753 |
|
|
Total long term investments |
|
|
248,515 |
|
|
|
(5 |
) |
|
|
248,510 |
|
|
|
193,835 |
|
|
|
(52 |
) |
|
|
193,783 |
|
|
Total investments |
|
$ |
304,690 |
|
|
$ |
(5 |
) |
|
$ |
304,685 |
|
|
$ |
301,170 |
|
|
$ |
(52 |
) |
|
$ |
301,118 |
|
|
|
1. |
Included in restricted cash and investments within the balance sheet as of December 31, 2016 is restricted cash and long term workers' compensation deposits of $4.8 million, which is excluded from the table above. |
F-18
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The following table summarizes the Company's financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis by fair value hierarchy level (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Recorded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Recorded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Basis |
|
|
Level 1 |
|
|
Level 2 |
|
|
Level 3 |
|
|
Other (1) |
|
|
Basis |
|
|
Level 1 |
|
|
Level 2 |
|
|
Level 3 |
|
|
Other (1) |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Cash Equivalents: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Money market funds |
|
$ |
1,943 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
1,943 |
|
|
$ |
21,312 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
21,312 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Investments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Certificates of deposit |
|
$ |
4,737 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
4,737 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|||||
|
Municipal bonds |
|
|
790 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
790 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,132 |
|
|
|
241 |
|
|
|
2,891 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||||
|
Corporate bonds |
|
|
790 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
790 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,946 |
|
|
|
2,291 |
|
|
|
655 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||||
|
Money market funds |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Restricted Cash and Investments: (2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Money market funds |
|
$ |
284,593 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
284,593 |
|
|
$ |
251,892 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
251,892 |
|
|||||
|
Certificates of deposit |
|
|
6,047 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,047 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
10,495 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
10,495 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||||
|
Corporate bonds |
|
|
2,888 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,888 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,972 |
|
|
|
2,285 |
|
|
|
687 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||||
|
Municipal bonds |
|
|
2,063 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,063 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,612 |
|
|
|
389 |
|
|
|
3,223 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||||
|
U.S. treasuries |
|
|
834 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
834 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,753 |
|
|
|
4,753 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||||
|
Total Investments |
|
$ |
304,685 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
18,149 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
286,536 |
|
|
$ |
301,118 |
|
|
$ |
9,959 |
|
|
$ |
17,951 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
273,208 |
|
|||||
|
(1) |
In accordance with ASU 2015-07, investments in money market funds measured at fair value using the NAV per share practical expedient are not subject to hierarchy level classification disclosure. The Company invests in money market funds that seek to maintain a stable net asset value. These investments include commingled funds that comprise high-quality short-term securities representing liquid debt and monetary instruments where the redemption value is likely to be the fair value. Redemption is permitted daily without written notice. |
|
(2) |
Included in restricted cash and investments within the balance sheet as of December 31, 2016 is restricted cash and long term workers' compensation deposits of $4.8 million, which is excluded from the table above. |
|
4. |
Property, Equipment and Software |
Property, equipment and software consist of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
Buildings |
|
$ |
15,250 |
|
|
$ |
13,988 |
|
|
Office furniture and fixtures |
|
|
8,693 |
|
|
|
7,808 |
|
|
Computer hardware and software |
|
|
15,719 |
|
|
|
12,887 |
|
|
Aircraft and other |
|
|
4,856 |
|
|
|
4,707 |
|
|
|
|
|
44,518 |
|
|
|
39,390 |
|
|
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization |
|
|
(19,335 |
) |
|
|
(18,060 |
) |
|
|
|
|
25,183 |
|
|
|
21,330 |
|
|
Land |
|
|
1,490 |
|
|
|
1,490 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
26,673 |
|
|
$ |
22,820 |
|
F-19
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
|
5. |
Workers' Compensation Claims |
The following table summarizes the aggregate workers' compensation reserve activity (in thousands):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Balance at January 1, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Workers' compensation claims liabilities |
|
$ |
255,675 |
|
|
$ |
225,278 |
|
|
$ |
121,056 |
|
|
Add: claims expense accrual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current year |
|
|
137,852 |
|
|
|
122,740 |
|
|
|
104,314 |
|
|
Prior years |
|
|
(301 |
) |
|
|
(13,683 |
) |
|
|
66,719 |
|
|
|
|
|
137,551 |
|
|
|
109,057 |
|
|
|
171,033 |
|
|
Less: claims payments related to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current year |
|
|
20,180 |
|
|
|
17,517 |
|
|
|
15,243 |
|
|
Prior years |
|
|
69,626 |
|
|
|
61,143 |
|
|
|
51,568 |
|
|
|
|
|
89,806 |
|
|
|
78,660 |
|
|
|
66,811 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Add: claims incurred in excess of retention limits |
|
|
9,117 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Workers' compensation claims liabilities |
|
$ |
312,537 |
|
|
$ |
255,675 |
|
|
$ |
225,278 |
|
|
Incurred but not reported (IBNR) |
|
$ |
158,169 |
|
|
$ |
127,792 |
|
|
$ |
113,984 |
|
The Company is a self-insured employer with respect to workers' compensation coverage for all of its employees (including employees co-employed through our client service agreements) working in Colorado, Maryland and Oregon, except as described below. In the state of Washington, state law allows only the Company's staffing services and internal management employees to be covered under the Company's self-insured workers' compensation program.
Effective January 1, 2015, the Company stopped maintaining a certificate to self-insure in the state of California, and it now obtains individual policies from Chubb for all California-based clients along with clients in Delaware, Virginia, Pennsylvania, North Carolina, New Jersey, West Virginia and the District of Columbia. The arrangement with Chubb, known as a fronted program, provides BBSI a licensed, admitted insurance carrier to issue policies on behalf of BBSI. The risk of loss up to the first $5.0 million per claim is retained by BBSI through a reinsurance agreement. Chubb assumes credit risk should BBSI be unable to satisfy its indemnification obligations.
As part of its fronted workers’ compensation insurance program with Chubb, the Company makes monthly payments into a trust account (“the Chubb trust account”) to be used for the payment of future claims. The balance in the Chubb trust account was $277.1 million and $166.6 million at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively. The Chubb trust account balances are included as a component of the current and long-term restricted cash and investments in the consolidated balance sheets.
The surplus of Ecole was $12.1 million and $9.5 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and is included in long-term restricted cash and investments in the consolidated balance sheets.
F-20
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The states of California, Maryland, Oregon, Washington, Colorado and Delaware required us to maintain specified investment balances or other financial instruments totaling $135.0 million and $156.8 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, to cover potential workers’ compensation claims losses related to the Company’s current and former status as a self-insured employer. In addition to restricted cash and investments held to satisfy these requirements, at December 31, 2016, we have provided surety bonds and standby letters of credit totaling $128.8 million, including a California requirement of $123.3 million.
The Company provided a total of $312.5 million and $255.7 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, as an estimated future liability for unsettled workers' compensation claims liabilities. Of this amount, $9.1 million represents case reserves incurred in excess of the Company’s retention limits at December 31, 2016. The accrual for costs incurred in excess of retention limits is offset by a receivable from excess insurance carriers of $9.1 million at December 31, 2016 that is included in other assets on the consolidated balance sheets. There was no workers’ compensation reserve in excess of retention limits in 2015.
|
6. |
Revolving Credit Facility and Long-Term Debt |
The Company maintains a credit agreement (the “Agreement”) with its principal bank, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association (the “Bank”). The Agreement provided for a $40.0 million term loan maturing December 31, 2016. The term loan has been completely paid off at December 31, 2016, compared to an outstanding balance of $15.0 million at December 31, 2015.
The Agreement was amended in December 2016 to increase our revolving credit line to $25.0 million, with a $6.0 million sublimit for standby letters of credit. Of the $6.0 million sublimit for standby letters of credit, $5.3 million was used at December 31, 2016. Advances under the revolving credit facility bear interest, as selected by the Company, of either (a) a daily floating rate of one month LIBOR plus 1.75% or (b) a fixed rate of LIBOR plus 1.75%. The Agreement also provides for an unused commitment fee of 0.35% per year through December 31, 2016 and 0.375% per year thereafter on the average daily unused amount of the revolving credit facility, and a fee of 1.75% of the face amount of each letter of credit reserved under the line of credit and 0.95% on standalone, fully secured letters of credit. The Company had no outstanding borrowings on its revolving credit line at December 31, 2016 and 2015. The line of credit expires on July 1, 2018.
The Agreement includes $5.0 million in standalone, cash-secured letters of credit at December 31, 2016 to satisfy collateral requirements associated with the Company’s former status as a self-insured employer in California. In conjunction with these letters of credit, the Company posted with the Bank as collateral $5.3 million in restricted certificates of deposit.
The credit facility is collateralized by the Company’s accounts receivable and other rights to receive payment, general intangibles, inventory and equipment.
The Agreement requires the satisfaction of certain financial covenants as follows:
|
|
• |
EBITDA [net profit before taxes plus interest expense (net of capitalized interest expense), depreciation expense, and amortization expense] on a rolling four-quarter basis of not less than $22 million at March 31, 2017 and $25 million at the end of each fiscal quarter thereafter; and |
F-21
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
|
|
• |
ratio of restricted and unrestricted cash and marketable securities to workers’ compensation and safety incentive liabilities of at least 1.0:1.0, measured quarterly on a rolling four-quarter basis. |
The Agreement includes certain additional restrictions as follows:
|
|
• |
capital expenditures may not exceed a total of $4.0 million in 2016 without the Bank’s prior approval; |
|
|
• |
incurring additional indebtedness is prohibited without the prior approval of the Bank, other than purchase financing (including capital leases) for the acquisition of assets, provided that the aggregate of all purchase financing does not exceed $1,000,000 at any time; and |
|
|
• |
the Company may not terminate or cancel any of the AICE policies without the Bank’s prior written consent. |
The Agreement also contains other customary events of default. If an event of default under the Agreement occurs and is continuing, the Bank may declare any outstanding obligations under the Credit Agreement to be immediately due and payable.
At December 31, 2016, the Company was in violation of the capital expenditure limitation. The Bank agreed to waive this covenant violation.
The Company maintains a mortgage loan with the Bank with a balance of approximately $4.6 million and $4.8 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, secured by the Company’s corporate office building in Vancouver, Washington. This loan requires payment of monthly principal payments of $18,375 plus interest at a rate of one month LIBOR plus 2.25%, with the unpaid principal balance due February 1, 2018.
|
7. |
401(k) Savings Plan |
We have a 401(k) Retirement Savings Plan for the benefit of our eligible employees. All staffing and management employees 21 years of age or older become eligible to participate in the savings plan upon completion of 1,000 hours of service in a consecutive 12-month period following the initial date of employment. Employees covered under a PEO arrangement may participate in the plan at the sole discretion of the PEO client. The determination of discretionary Company contributions to the plan, if any, is at the sole discretion of our Board of Directors. No discretionary Company contributions were made to the plan for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014.
We make matching contributions to the 401(k) plan under a safe harbor provision, whereby the Company matches 100% of contributions by management and staffing employees up to 3% of each participating employee's annual compensation; and 50% of the employee's contributions up to an additional 2% of annual compensation. We made $1,402,000, $1,158,000, and $885,000 of matching contributions during 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Participants' interests in Company safe harbor contributions to the plan are fully vested when payments are made.
F-22
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
|
8. |
Commitments |
We lease office space for our branch offices under operating lease agreements that require minimum annual payments as follows (in thousands):
|
Year Ending |
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
|
|
2017 |
|
$ |
4,101 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
3,379 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2,436 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
1,651 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
1,003 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
754 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
13,324 |
|
Rent expense was approximately $4.5 million, $4.1 million, and $3.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
|
9. |
Income Taxes |
The provision (benefit) for income taxes from operations is as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|
2014 |
|
|||
|
Current: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
$ |
6,442 |
|
|
$ |
5,833 |
|
|
$ |
(7,058 |
) |
|
State |
|
|
2,030 |
|
|
|
921 |
|
|
|
(640 |
) |
|
|
|
|
8,472 |
|
|
|
6,754 |
|
|
|
(7,698 |
) |
|
Deferred: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
|
85 |
|
|
|
1,854 |
|
|
|
(10,294 |
) |
|
State |
|
|
(1,770 |
) |
|
|
1,044 |
|
|
|
894 |
|
|
|
|
|
(1,685 |
) |
|
|
2,898 |
|
|
|
(9,400 |
) |
|
Total provision (benefit) |
|
$ |
6,787 |
|
|
$ |
9,652 |
|
|
$ |
(17,098 |
) |
F-23
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities consist of the following components (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
||
|
Deferred income tax assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Workers' compensation claims liabilities |
|
$ |
11,477 |
|
|
$ |
11,190 |
|
|
MCC accrual |
|
|
4,561 |
|
|
|
3,532 |
|
|
Safety incentives payable |
|
|
7,779 |
|
|
|
5,851 |
|
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts |
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
109 |
|
|
Deferred compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
219 |
|
|
Equity based compensation |
|
|
991 |
|
|
|
719 |
|
|
Tax effect of unrealized losses, net |
|
|
(17 |
) |
|
|
(3 |
) |
|
Alternative minimum tax credit carryforward |
|
|
1,648 |
|
|
|
1,831 |
|
|
State credit carryforward |
|
|
868 |
|
|
|
712 |
|
|
Other |
|
|
765 |
|
|
|
436 |
|
|
|
|
|
28,103 |
|
|
|
24,596 |
|
|
Less valuation allowance |
|
|
216 |
|
|
|
216 |
|
|
|
|
|
27,887 |
|
|
|
24,380 |
|
|
Deferred income tax liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tax depreciation in excess of book depreciation |
|
|
(5,319 |
) |
|
|
(4,243 |
) |
|
Tax amortization of goodwill |
|
|
(13,191 |
) |
|
|
(12,395 |
) |
|
Other |
|
|
(7 |
) |
|
|
(57 |
) |
|
|
|
|
(18,517 |
) |
|
|
(16,695 |
) |
|
Net deferred income tax assets |
|
$ |
9,370 |
|
|
$ |
7,685 |
|
F-24
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The effective tax rate for operations differed from the U.S. statutory federal tax rate due to the following:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
|
2015 |
|
|
|
2014 |
|
|
|||
|
Statutory federal tax rate |
|
|
35.0 |
|
% |
|
|
35.0 |
|
% |
|
|
(35.0 |
) |
% |
|
State taxes, net of federal benefit |
|
|
1.1 |
|
|
|
|
4.3 |
|
|
|
|
.6 |
|
|
|
Valuation allowance on capital loss carryforward and state tax credit carryforward |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
(2.1 |
) |
|
|
|
(.2 |
) |
|
|
Adjustment for final positions on filed returns |
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
(3.5 |
) |
|
|
|
(.8 |
) |
|
|
Nondeductible expenses and other, net |
|
|
1.8 |
|
|
|
|
6.1 |
|
|
|
|
3.6 |
|
|
|
Federal tax-exempt interest income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
(.1 |
) |
|
|
|
(.2 |
) |
|
|
Federal and state tax credits |
|
|
(11.6 |
) |
|
|
|
(14.3 |
) |
|
|
|
(6.9 |
) |
|
|
Other, net |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
2.1 |
|
|
|
|
(1.2 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
26.5 |
|
% |
|
|
27.5 |
|
% |
|
|
(40.1 |
) |
% |
The realization of a significant portion of net deferred tax assets is based in part on our estimates of the timing of reversals of certain temporary differences and on the generation of taxable income before such reversals.
Under ASC 740, “Income Taxes,” management evaluates the realizability of the deferred tax assets on a quarterly basis under a “more-likely than not” standard. As part of this evaluation, management reviews all evidence both positive and negative to determine if a valuation allowance is needed. One component of this analysis is to determine whether the Company was in a cumulative loss position for the most recent 12 quarters. The Company was in a cumulative income position for the 12 quarters ended at both December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015.
The Company is subject to income taxes in U.S. federal and multiple state and local tax jurisdictions. The Internal Revenue Service is examining the Company’s federal tax returns for the years ended December 31, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014. In the major jurisdictions where it operates, the Company is generally no longer subject to income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2011. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits.
A portion of the consolidated income the Company generates is not subject to state income tax. Depending on the percentage of this income as compared to total consolidated income, the Company's state effective rate could fluctuate from expectations.
At December 31, 2016, the Company did not have a federal general business tax credit carry forward. The Company had an alternative minimum tax credit carry forward of approximately $1.6 million which has an indefinite life and will not expire until utilized.
At December 31, 2016, the Company had state tax credit carry forwards of approximately $868,000 which expire unless utilized in tax years on or before December 31, 2025.
|
10. |
Stock Incentive Plans |
The Company's 2015 Stock Incentive Plan (the "2015 Plan"), which provides for stock-based awards to Company employees, non-employee directors and outside consultants or advisors, was approved by stockholders on May 27, 2015. The number of shares of common stock reserved for issuance under the 2015 Plan is 1,000,000, of which the
F-25
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
maximum number of shares for which incentive stock options may be granted is 900,000. The 2015 Plan replaced the Company’s 2009 Stock Incentive Plan (the “2009 Plan”), and no new stock-based awards may be granted under the 2009 Plan. The number of shares available for grant at December 31, 2016 is 792,795. Outstanding option awards under all the plans generally expire ten years after the date of grant.
Stock-based compensation expense included in selling, general and administrative expenses during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, was $2.8 million, $2.4 million and $1.7 million, respectively. Related income tax benefits for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, were $1.1 million, $948,000 and $675,000, respectively.
Stock Options
Stock options are generally exercisable in four equal annual installments beginning one year following the date of grant.
A summary of the status of the Company’s stock options at December 31, 2016, together with changes during the periods then ended, is presented below:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
Average |
|
|
Aggregate |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
Remaining |
|
|
Intrinsic |
|
|||||
|
|
|
Number |
|
|
Exercise |
|
|
Contractual |
|
|
Value |
|
||||||
|
|
|
of Options |
|
|
Price |
|
|
Term (years) |
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||||
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
|
|
360,100 |
|
|
$ |
17.35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Options granted at market price |
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
39.80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Options exercised |
|
|
(4,400 |
) |
|
|
14.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Options cancelled |
|
|
(62,500 |
) |
|
|
18.56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
303,200 |
|
|
|
17.89 |
|
|
|
4.53 |
|
|
|
14,012 |
|
||
|
Exercisable at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
206,950 |
|
|
$ |
15.44 |
|
|
|
3.86 |
|
|
$ |
10,069 |
|
||
The weighted average fair value of stock options granted for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, was $17.10 and $10.76, respectively. There were no stock options granted with an exercise price below market price during 2016 and 2015. No stock options were granted during 2014.
The intrinsic value of stock options exercised for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, was $113,000, $1.1 million and $1.0 million, respectively. The fair value of shares vested for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, was $319,000, $383,000 and $534,000, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, unrecognized compensation expense related to stock options was $718,000 with a weighted average remaining amortization period of 2.5 years.
Restricted Stock Units
Restricted stock units vest in four equal annual installments beginning one year following the date of grant.
F-26
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The following table presents restricted stock unit activity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grant Date |
|
|||
|
|
|
Units |
|
|
Fair Value |
|
||||
|
Nonvested at December 31, 2015 |
|
|
150,811 |
|
|
$ |
42.74 |
|
||
|
Granted |
|
|
150,780 |
|
|
|
41.72 |
|
||
|
Vested |
|
|
(35,604 |
) |
|
|
40.67 |
|
||
|
Cancelled/Forfeited |
|
|
(37,112 |
) |
|
|
42.19 |
|
||
|
Nonvested at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
228,875 |
|
|
$ |
42.48 |
|
||
The total fair value of shares vested during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, was $1.9 million, $1.7 million and $820,000, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, unrecognized compensation expense related to restricted stock units was $8.1 million with a weighted average remaining amortization period of 3.0 years.
|
11. |
Stock Repurchase Program |
The Company maintains a stock repurchase program approved by the Board of Directors, which authorizes the repurchase of shares from time to time in open market purchases. The repurchase program currently allows for the repurchase of approximately 1.1 million additional shares as of December 31, 2016.
No share repurchases were made under the repurchase program during 2016 and 2015.
|
12. |
Litigation |
On November 6, 2014, plaintiffs in Michael Arciaga, et al. v. Barrett Business Services, Inc., et al., filed an action in the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington against BBSI, Michael L. Elich, BBSI’s Chief Executive Officer, and James D. Miller, BBSI’s then Chief Financial Officer. The action purported to be a class action brought on behalf of all BBSI shareholders alleging violations of the federal securities laws. The claims arose from the decline in the market price for BBSI common stock following announcement of a charge for increased workers’ compensation reserves expense. The lawsuit sought compensatory damages, plus interest, and costs and expenses (including attorney fees and expert fees).
On November 13, 2014, a second purported shareholder class action was filed in the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington, entitled Christopher P. Carnes, et al. v. Barrett Business Services, Inc., et al. The Carnes complaint named the same defendants as the Arciaga case and asserted similar claims for relief.
Similarly, on November 17, 2014, a third purported shareholder class action was filed in the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington, entitled Shiva Stein, et al. v. Barrett Business Services, Inc., et al. The Stein complaint named the same defendants as the Arciaga and Carnes cases and asserted similar claims for relief.
On February 25, 2015, the court ordered consolidation of the three cases, and any new or other cases involving the same subject matter, into a single action for pretrial purposes. The consolidated cases were recaptioned as In re Barrett Business Services
F-27
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Securities Litigation. The court also appointed the Painters & Allied Trades District Council No. 35 Pension and Annuity Funds as the lead plaintiff.
On March 21, 2016, before the court had ruled on the defendants’ motion to dismiss the plaintiffs’ first amended consolidated complaint, the plaintiffs filed a second amended consolidated complaint, naming the same defendants. The second amended consolidated complaint dropped certain allegations from the first amended complaint and added new allegations relating to disclosures in BBSI’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 9, 2016. The defendants filed a motion to dismiss the second amended consolidated complaint on May 23, 2016.
On October 26, 2016, before the court ruled on the motion to dismiss, the parties entered into a Stipulation and Agreement of Settlement dated as of October 26, 2016 (the “Settlement”), to settle the litigation. The settlement class includes all persons and entities who purchased or otherwise acquired BBSI common stock in the period beginning February 12, 2013, through March 9, 2016, and were damaged thereby, with certain exclusions.
The Settlement is intended to fully, finally and forever compromise, settle, release, resolve, and dismiss with prejudice the purported class action and all claims asserted therein against the named defendants. In the Settlement, the defendants have denied all allegations of wrongdoing and the plaintiffs have not conceded any infirmities in their positions.
The Settlement called for the payment in cash of $12.0 million (the “Settlement Fund”) into escrow by November 29, 2016. Of this amount, approximately $8.7 million was paid by BBSI’s insurance carriers and approximately $3.3 million was paid by BBSI.
The Settlement is subject to approval by the court and to other customary terms and conditions. All potential class members were notified of the Settlement in November 2016, and no requests to opt out of the class were received by the deadline. Final approval of the settlement was received at a court hearing held on February 22, 2017. The fees of counsel for the plaintiffs will be paid out of the Settlement Fund following approval by the court.
BBSI received a subpoena from the San Francisco office of the Division of Enforcement of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) in May 2015 in connection with the SEC’s investigation of BBSI’s accounting practices with regard to its workers’ compensation reserves. In April 2016, the SEC issued a second subpoena to BBSI for documents relating to the disclosures made by BBSI following Mr. Miller’s termination. BBSI was also advised by the United States Department of Justice in mid-June 2016 that it has commenced an investigation. BBSI is cooperating fully with the investigations.
On June 17, 2015, Daniel Salinas (“Salinas”) filed a shareholder derivative lawsuit against BBSI and certain of its officers and directors in the Circuit Court for Baltimore City, Maryland. The complaint alleges breaches of fiduciary duty, unjust enrichment and other violations of law and seeks recovery of various damages, including the costs and expenses incurred in connection with BBSI’s reserve strengthening process, reserve study and consultants, the cost of stock repurchases by BBSI in October 2014, compensation paid to BBSI’s officers, and costs of negotiating BBSI’s credit facility with its principal lender, as well as the proceeds of sales of stock by certain of BBSI’s officers and directors during 2013 and 2014. On September 28, 2015, BBSI and the individual defendants filed motions
F-28
Barrett Business Services, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
to dismiss the derivative suit and a motion to stay pending resolution of In re Barrett Business Services Securities Litigation. On December 4, 2015, Salinas filed an opposition to each motion. On January 27, 2016, the defendants filed a reply to the opposition brief. On February 11, 2016, Judge Michel Pierson heard oral argument on the motions. A decision has not been issued.
Management is unable to estimate the probability, or the potential range of loss arising from the legal actions described above.
BBSI is subject to other legal proceedings and claims, which arise in the ordinary course of our business. In the opinion of management, the amount of ultimate liability with respect to other currently pending or threatened actions is not expected to materially affect BBSI’s consolidated financial position or results of operations.
|
13. |
Quarterly Financial Information (Unaudited) |
(in thousands, except per share amounts and market price per share)
|
|
|
Quarter Ended |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
March 31 |
|
|
June 30 |
|
|
September 30 |
|
|
December 31 |
|
||||
|
Year ended December 31, 2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
190,968 |
|
|
$ |
203,417 |
|
|
$ |
225,103 |
|
|
$ |
221,098 |
|
|
Cost of revenues |
|
|
180,581 |
|
|
|
161,164 |
|
|
|
175,544 |
|
|
|
177,761 |
|
|
Gross Margin |
|
|
10,387 |
|
|
|
42,253 |
|
|
|
49,559 |
|
|
|
43,337 |
|
|
Net (loss) income |
|
|
(8,003 |
) |
|
|
8,522 |
|
|
|
10,233 |
|
|
|
8,047 |
|
|
Basic (loss) earnings per share |
|
|
(1.11 |
) |
|
|
1.18 |
|
|
|
1.41 |
|
|
|
1.11 |
|
|
Diluted (loss) earnings per share |
|
|
(1.11 |
) |
|
|
1.16 |
|
|
|
1.38 |
|
|
|
1.08 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
166,400 |
|
|
$ |
181,959 |
|
|
$ |
198,725 |
|
|
$ |
193,757 |
|
|
Cost of revenues |
|
|
157,469 |
|
|
|
145,481 |
|
|
|
155,835 |
|
|
|
152,600 |
|
|
Gross Margin |
|
|
8,931 |
|
|
|
36,478 |
|
|
|
42,890 |
|
|
|
41,157 |
|
|
Net (loss) income |
|
|
(5,828 |
) |
|
|
8,902 |
|
|
|
10,973 |
|
|
|
11,447 |
|
|
Basic (loss) earnings per share |
|
|
(0.82 |
) |
|
|
1.24 |
|
|
|
1.52 |
|
|
|
1.59 |
|
|
Diluted (loss) earnings per share |
|
|
(0.82 |
) |
|
|
1.21 |
|
|
|
1.49 |
|
|
|
1.55 |
|
|
14. |
Subsequent Events |
|
We have evaluated events and transactions occurring after the balance sheet date through our filing date and noted no events that are subject to recognition or disclosure. |
F-29
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
|
BARRETT BUSINESS SERVICES, INC. |
|
|
|
|
Registrant |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: March 8, 2017 |
|
By: |
/s/ Gary E. Kramer |
|
|
|
|
Gary E. Kramer Vice President-Finance, Treasurer and Secretary |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities indicated on the 8th day of March, 2017.
|
Principal Executive Officer and Director: |
||
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Michael L. Elich |
|
President and Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
Michael L. Elich |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Principal Financial and Accounting Officer: |
||
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Gary E. Kramer |
|
Vice President-Finance, Treasurer and Secretary |
|
Gary E. Kramer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Majority of Directors: |
||
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Thomas J. Carley |
|
Director |
|
Thomas J. Carley |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Thomas B. Cusick |
|
Director |
|
Thomas B. Cusick |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ James B. Hicks |
|
Director |
|
James B. Hicks, Ph.D. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Roger L. Johnson |
|
Director |
|
Roger L. Johnson |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Jon L. Justesen |
|
Director |
|
Jon L. Justesen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Anthony Meeker |
|
Chairman of the Board and Director |
|
Anthony Meeker |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Vincent P. Price |
|
Director |
|
Vincent P. Price |
|
|
|
3.1 |
Charter of the Registrant, as amended, through March 27, 2012. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2012. |
|
3.2 |
Bylaws of the Registrant, as amended through December 17, 2015. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 22, 2015. |
|
4.1 |
Credit Agreement dated as of December 29, 2014, between the Registrant and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association (“Wells Fargo”). Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 5, 2015. |
|
4.2 |
First Amendment to Credit Agreement dated as of August 27, 2015, between the Registrant and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2016 (the “2016 First Quarter 10-Q”). |
|
4.3 |
Second Amendment to Credit Agreement dated as of December 30, 2015, between the Registrant and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the 2016 First Quarter 10-Q. |
|
4.4 |
Third Amendment to Credit Agreement dated as of April 15, 2016, between the Registrant and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report for the quarter ended June 30, 2016 (the” 2016 Second Quarter 10-Q”). |
|
4.5 |
Fourth Amendment to Credit Agreement dated as of June 28, 2016, between the Registrant and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the 2016 Second Quarter 10-Q. |
|
4.7 |
Fifth Amendment to Credit Agreement dated as of December 28, 2016, between the Registrant and Wells Fargo. |
|
4.8 |
Revolving Line of Credit Note dated December 28, 2016, of the Registrant. |
|
4.9 |
Term Note dated November 1, 2012, of the Registrant. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2012 (the “2012 Third Quarter 10-Q”). |
|
4.10 |
First Modification to Term Note dated December 29, 2014, of the Registrant. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 5, 2015 (the “January 2015 8-K”). |
|
4.11 |
Second Modification to Promissory (Term) Note dated as of December 28, 2016, of the Registrant. |
|
4.12 |
Security Agreement: Specific Rights to Payment dated as of June 14, 2013, between the Registrant and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2013. |
|
4.13 |
Standby Letter of Credit Agreement dated as of September 18, 2012 between the Registrant and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the 2012 Third Quarter 10-Q. |
|
4.14 |
Second Amended and Restated Third Party Security Agreement: Specific Rights to Payment dated as of December 29, 2014, between Associated Insurance Company for Excess (“AICE”) and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.7 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10‑K for the year ended December 31, 2014. |
|
4.15 |
First Amendment to Second Amended and Restated Third Party Security Agreement: Specific Rights to Payment dated as of August 27, 2015, between AICE and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the 2016 First Quarter 10-Q. |
|
4.16 |
Second Amendment to Second Amended and Restated Third Party Security Agreement: Specific Rights to Payment dated as of December 30, 2015, between AICE and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the 2016 First Quarter 10-Q. |
|
4.17 |
Third Amendment to Second Amended and Restated Third Party Security Agreement: Specific Rights to Payment dated as of April 15, 2016, between AICE and Wells Fargo. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the 2016 Second Quarter 10-Q. |
The Registrant has incurred additional long-term indebtedness as to which the amount involved is less than 10 percent of the Registrant's total assets. The Registrant agrees to furnish copies of the instruments relating to such indebtedness to the Commission upon request.
|
10.1 |
Second Amended and Restated 1993 Stock Incentive Plan of the Registrant. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2001.* |
|
10.2 |
2003 Stock Incentive Plan of the Registrant (the "2003 Plan"). Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2003.* |
|
10.3 |
Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement under the 2003 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10‑K for the year ended December 31, 2003.* |
|
10.4 |
Form of Incentive Stock Option Award Agreement relating to January 2009 option grants under the 2003 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (the “2008 10-K”).* |
|
10.5 |
Form of Employee Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement relating to January 2009 option grants under the 2003 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the 2008 10-K.* |
|
10.6 |
Form of Non-Employee Director Option Award Agreement relating to January 2009 option grants under the 2003 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 to the 2008 10-K.* |
|
10.7 |
2009 Stock Incentive Plan of the Registrant (the “2009 Plan”). Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2009.* |
|
10.8 |
Form of Incentive Stock Option Award Agreement under the 2009 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2010 (the “2010 First Quarter 10-Q”).* |
|
10.9 |
Form of Employee Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement under the 2009 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the 2010 First Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.10 |
Form of Non-Employee Director Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement under the 2009 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the 2010 First Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.12 |
Form of Employee Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement under the 2009 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the 2011 First Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.13 |
Form of Non-Employee Director Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement under the 2009 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the 2011 First Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.14 |
Form of Employee Restricted Stock Units Award Agreement under the 2009 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the 2012 Third Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.15 |
Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Units Award Agreement under the 2009 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the 2012 Third Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.16 |
Form of Incentive Stock Option Award Agreement relating to February 2, 2015, grants under the 2009 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2015 (the “2015 10-K”).* |
|
10.17 |
2015 Stock Incentive Plan of the Registrant (the "2015 Plan"). Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8‑K filed on June 2, 2015.* |
|
10.18 |
Form of Employee Restricted Stock Units Award Agreement for Executive Officers under the 2015 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10‑Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2015 (the "2015 Second Quarter 10-Q").* |
|
10.19 |
Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Units Award Agreement under the 2015 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the 2015 Second Quarter 10‑Q.* |
|
10.20 |
Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Units Award Agreement for awards granted during 2016 under the 2015 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2016 (the “2016 Third Quarter 10-Q”).* |
|
10.21 |
Form of Employee Restricted Stock Units Award Agreement for Executive Officers for awards granted during 2016 under the 2015 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the 2016 Third Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.22 |
Form of Performance Share Award Agreement for Executive Officers for awards granted under the 2015 Plan. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the 2016 Third Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.23 |
Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement between the Registrant and Thomas J. Carley dated July 1, 2016. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the 2016 Third Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.24 |
Amendment to each outstanding Employee Restricted Stock Units Award Agreement for Executive Officers effective January 30, 2017.* |
|
10.25 |
Summary of compensatory arrangements for non-employee directors of the Registrant.* |
|
10.26 |
Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Michael L. Elich, dated September 25, 2001. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Registrant's Registration Statement on Form S-2 (Registration No. 333-126496) filed July 11, 2005.* |
|
10.27 |
Change in Control Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Michael L. Elich, dated April 12, 2011. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the 2011 First Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.28 |
Change in Control Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Gregory R. Vaughn, dated April 12, 2011. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the 2011 First Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.29 |
Change in Control Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Gerald R. Blotz, dated June 16, 2015. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the 2015 Second Quarter 10‑Q.* |
|
10.30 |
Change in Control Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Gary E. Kramer, dated August 19, 2016. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the 2016 Third Quarter 10-Q.* |
|
10.31 |
Death Benefit Agreement entered into by the Registrant and Michael L. Elich effective January 1, 2014. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.27 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2013 (the “2013 10-K”).* |
|
10.32 |
Death Benefit Agreement entered into by the Registrant and Gregory R. Vaughn effective January 1, 2014. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.28 to the 2013 10-K.* |
|
10.33 |
Death Benefit Agreement entered into by the Registrant and Gerald L. Blotz effective July 17, 2015. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.27 to the 2015 10-K.* |
|
10.34 |
Barrett Business Services, Inc. Annual Cash Incentive Award Plan, Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 13, 2014.* |
|
10.35 |
Form of Indemnification Agreement with each outside director of Barrett Business Services, Inc.* |
|
10.36 |
Form of Indemnification Agreement between the Registrant and each of Michael Elich, James Miller and Gregory Vaughn effective in September 2015. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.30 to the 2015 10-K.* |
|
10.37 |
Indemnification Agreement between the Registrant and Michael Elich dated as of November 19, 2015. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.31 to the 2015 10-K.* |
|
10.38 |
Indemnification Agreement between the Registrant and James D. Miller dated as of November 19, 2015. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.32 to the 2015 10-K.* |
|
21. |
Subsidiaries of the Registrant. |
|
23.1 |
Consent of Deloitte & Touche LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
|
23.2 |
Consent of Moss Adams LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
|
31.1 |
Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a). |
|
31.2 |
Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a). |
|
32. |
Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350. |
|
99.1 |
Description of the Registrant's capital stock. Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the 2015 Second Quarter 10‑Q.* |
|
101. |
INS XBRL Instance Document |
|
101. |
SCH XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
|
101. |
CAL XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
|
101. |
DEF XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
|
101. |
LAB XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
|
101. |
PRE XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
|
* |
Denotes a management contract or a compensatory plan or arrangement. |
|
** |
Except as otherwise indicated, the SEC File Number for all exhibits is 000-21866. |